Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TM4C123GH6PM, ENERGIA
Hello,
I'm trying to transmit data through I2C. However I can't seem to get it to work.
Using CCS Version 10.3.0.00007 , I replicated the Programming Example under 16.3 of the peripheral user guide, provided by TI, see link:
I'll attach my code:
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "driverlib/debug.h"
#include "driverlib/fpu.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "driverlib/rom.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/timer.h"
#include "driverlib/i2c.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The error routine that is called if the driver library encounters an error.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#ifdef DEBUG
void
__error__(char *pcFilename, uint32_t ui32Line)
{
}
#endif
void ConfigureI2CasMaster()
{
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_I2C0);
while (!SysCtlPeripheralReady(SYSCTL_PERIPH_I2C0))
{
}
// set bus speed and enable master
I2CMasterInitExpClk(I2C0_BASE, SysCtlClockGet(), true);
I2CMasterSlaveAddrSet(I2C0_BASE, 0x3B, false);
I2CMasterDataPut(I2C0_BASE, 'Q');
I2CMasterControl(I2C0_BASE, I2C_MASTER_CMD_SINGLE_SEND);
while (I2CMasterBusBusy(I2C0_BASE))
{
}
}
void SendI2CData()
{
I2CMasterDataPut(I2C0_BASE, 'Q');
I2CMasterControl(I2C0_BASE, I2C_MASTER_CMD_SINGLE_SEND);
while (I2CMasterBusBusy(I2C0_BASE))
{
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// main
//
//*****************************************************************************
int main(void)
{
// Setup the system clock to run at 40 MHz from PLL with crystal reference
ROM_SysCtlClockSet(SYSCTL_SYSDIV_5 | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_XTAL_16MHZ |
SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN);
ConfigureI2CasMaster();
// enter the Loop
while (1)
{
SysCtlDelay(10000);
SendI2CData();
}
}
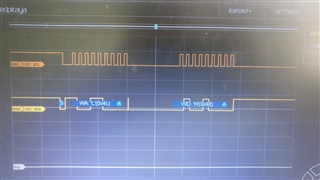
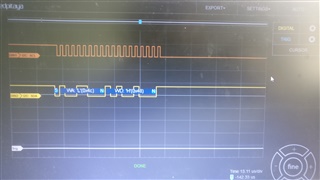
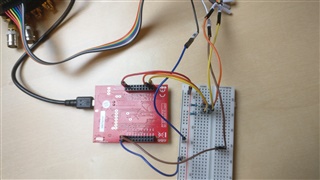
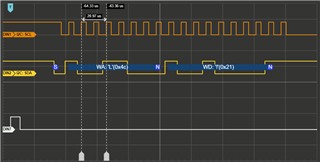
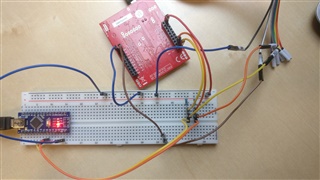
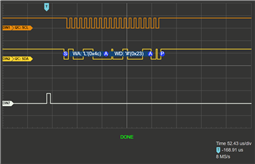
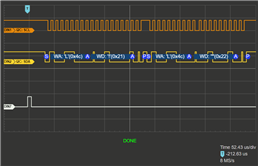
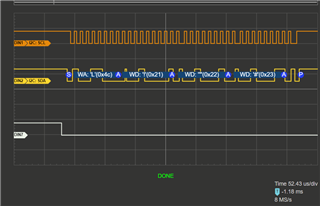
I have a logic analyzer on pin B2 and B3, which are SCL0 and SDA0 on the TM4c123GXL Board.
GND is connected and the logic analyzer is set up properly. (tested on a different device)
I would expect my code to repeatedly transmit data, however my logic analyzer shows me that absolutely nothing happens.
Is something wrong with my code?
Thank you