Part Number: TMDSCNCD28388D
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: C2000WARE
HI, Yashwant Temburu1
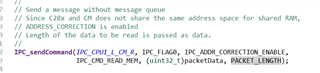
Please tell me. In the above function, the data and address are sent to the CM4 core through IPC. My own data is placed in the following array send_buff[150]. Can I directly replace the packetData in the function with send_buff?
I saw in the comment of the function that packetData corresponds to the address, and PACKET_LENGTH corresponds to the data.
This comment confuses me a bit.
My current progress is that the project that needs to be run by the CPU1 core has been improved, and the project for the CM4 core is also ready. Next, as long as the http file in the web service is changed, the data received by CM4 can be sent to the web page with the computer IP address of 192.168.0.4 via ethernet and displayed in real time?
thanks
vince