Part Number: TMS320F28388D
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: HALCOGEN, C2000WARE
I am starting to implement an emulation EEPROM (Fee) on TMS320F28388D and I only found this thread as a support material.
I am planning to start from the example which is included in HALCoGen tool (http://www.ti.com/tool/HALCOGEN) for the device “TMS570LS31x_21x” (\ti\Hercules\HALCoGen\v04.07.01\examples\TMS570LS31x_21x\example_TI_Fee_Write_Read)
Is it the right starting path ?
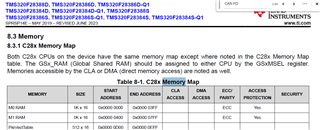
Another problem is I can not find the memory layout in the user-manual, do you have guidelines where to find it?