Tool/software:
Hi,
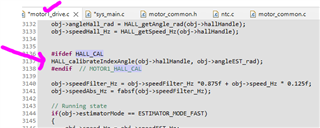
As part of taking my e Bike BLDC Motor controller to production, during commisioning of one type of motor , would like controller to identify the Hall sensor (A, B or C ) Sequence ...
That is once motor phase wire and hall feedback wires are conected in any sequence, once I run the sequence identification routine, it should identify which iinput is HALL A, Which one is Hall B and which one is HALL C even if they are not connected in a proper sequence.
Please suggest how to do this in universal motor controller project.
Thanks in advance.
Regards,
Anil