Hello.
I use F28M35H52C1 Concerto Control Card with dockStantion. Code Composer Studio Version: 5.5.0.00077.
Four days I tried launch PWM. And I got some result, but not finished. Help me please =(. I don't understand where I made mistake.
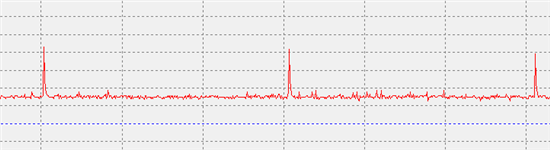
My scope show me next signal from PWM1A :
But I set PERIOD =1000 and DUTY_CYCLE=500.
Below I attached my code:
/*
* main.c
*/
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
#define DUTY_CYCLE 500
#define PERIOD 1000
void ConfigEpwm1( void );
int main(void)
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// Enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the F28M35x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
// Step 2. Initalize GPIO:
InitEPwm1Gpio();
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 0; // Stop all the TB clocks
EDIS;
ConfigEpwm1();
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 1; // Start all the timers synced
EDIS;
for(;;)
{
asm (" NOP");
}
}
void ConfigEpwm1( void )
{
// Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl();
EALLOW;
// Configure PWM timers
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = PERIOD; // Period = 1201 TBCLK counts
EPwm1Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0; // Set Phase register to zero
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UP; // Asymmetrical mode
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE; // Phase loading disabled
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.PRDLD = TB_SHADOW;
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.SYNCOSEL = TB_SYNC_DISABLE;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWAMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWBMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADAMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO; // load on CTR=Zero
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADBMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO; // load on CTR=Zero
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLA.bit.PRD = AQ_CLEAR;
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_SET;
//EPwm1Regs.CMPC = DUTY_CYCLE;
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA=DUTY_CYCLE;
// EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
// EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = PWM1_INT_ENABLE; // Enable INT
//EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_1ST; // Generate INT on 1st event
EDIS;
}
And next code from M3:
int main(void)
{
int i = 0;
// Allow writes to protected registers.
HWREG(SYSCTL_MWRALLOW) = 0xA5A5A5A5;
// Sets up PLL, M3 running at 75MHz and C28 running at 150MHz
SysCtlClockConfigSet(SYSCTL_USE_PLL | (SYSCTL_SPLLIMULT_M & 0xF) |
SYSCTL_SYSDIV_1 | SYSCTL_M3SSDIV_2 |
SYSCTL_XCLKDIV_4);
// Enable all GPIOs
// PinoutSet();
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
// Enable Pullups on EPWM(1-8)A/B capable pins
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, 0xFF, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD_WPU);
// GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, 0xFF, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD_WPU);
// Give C28 control of all GPIOs
GPIOPinConfigureCoreSelect(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, 0xFF, GPIO_PIN_C_CORE_SELECT);
// Unlock the register to change the commit register value for Port B Pin 7
// This disables the NMI functionality on the pin and allows other muxing
// options to be used
HWREG(GPIO_PORTB_BASE+GPIO_O_LOCK) = GPIO_LOCK_KEY_DD;
// Write to commit register
HWREG(GPIO_PORTB_BASE+GPIO_O_CR) |= 0x000000FF;
// Delay
for (i=0;i<20;i++){};
IPCMtoCBootControlSystem(CBROM_MTOC_BOOTMODE_BOOT_FROM_FLASH);
// Disable clock supply for the watchdog modules
SysCtlPeripheralDisable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_WDOG1);
SysCtlPeripheralDisable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_WDOG0);
//Enable processor interrupts.
IntMasterEnable();
// Main Code
while(1) ;
}