Tool/software:
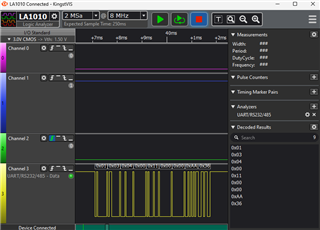
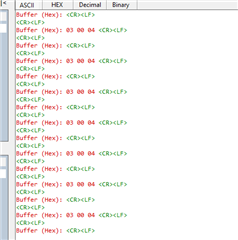
I'm snipping the data from the modbus system. I can see the value using logic analyser but it doesn't come up serial terminal.
I tried to print normal string it's working but the data which in buffer never comes up to serial terminal?
Correct me if I'm wrong. The chip I'm using, MSP430FR5987, is inserted in a circuit that is for a specific project. Im using 19200 baud rate, is it the reason im not getting those buffer value in the serial terminal?
I've watched a video tutorial to mentioning that if i want to use baud rate higher than 9600, i have to use USB to UART converter (FT232RL).
Looking for your valuable advise and suggestions.
Thanks