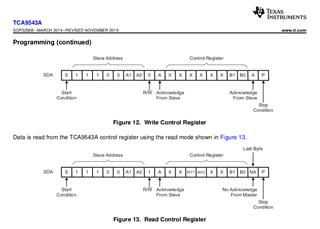
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TCA9543A, TCA9534A
Tool/software:
Hi Team,
I am using MSP430-FR-2475 MCU as a I2C master with 400Khz speed and one I2C slave is connected to it with unknown slave address.
Can you please suggest the exact code to know the I2C slave address of this slave device?
Generally we have to provide start I2C, then send address values one by one in for loop and whichever address value is acknowleged is considered as slave address. But in firmware exactly how to implement this i am confused. Can you please help here?