Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TPS25750
Hi team,
Can you have a look at below customer inquiry please?
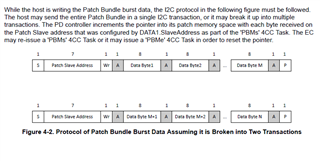
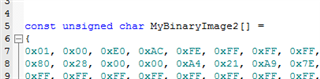
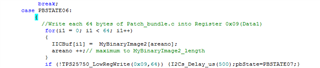
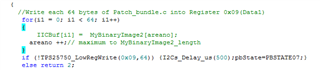
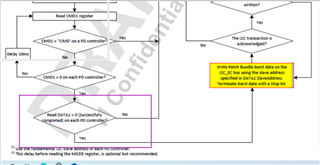
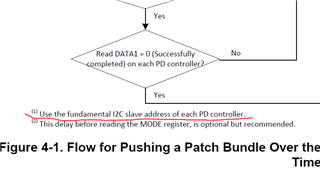
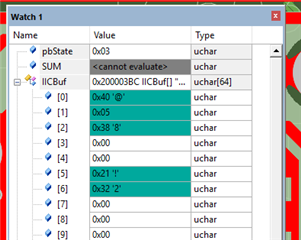
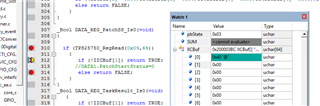
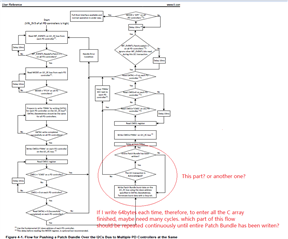
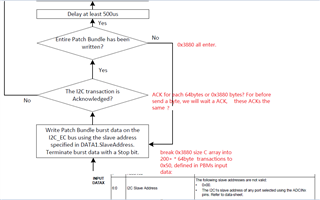
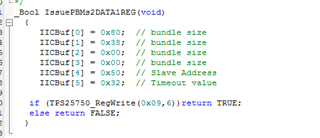
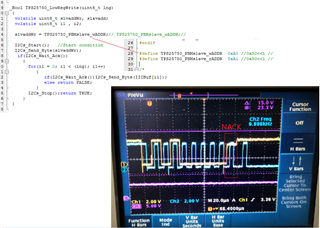
I cannot access the GUI. Otherwise, the bin file generated from GUI maybe un-useful for me, for I want to configure the PD controller via the I2Cs port with a MCU.
Could you please help to reply these questions below?
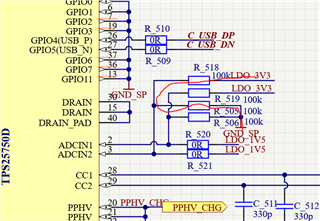
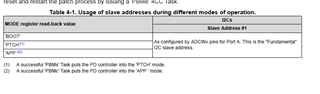
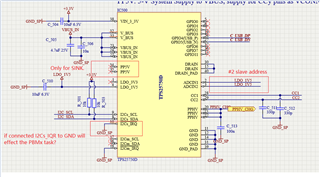
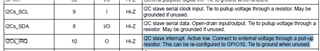
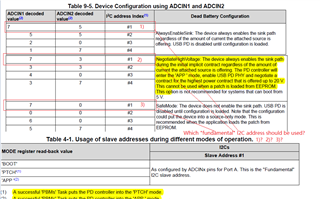
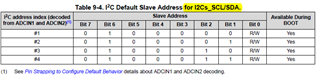
- Is the Slave address, maybe one of #1,#2,#3,#4 which was configured from ADCIN1&ADCIN2, the Unique address?
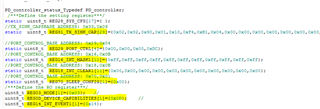
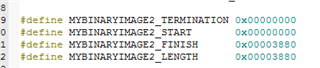
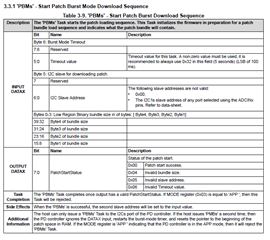
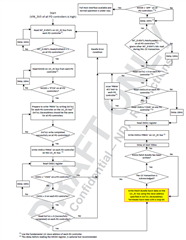
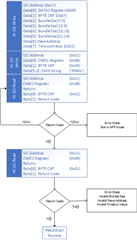
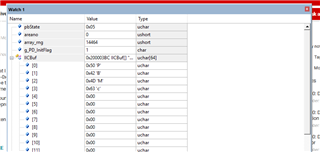
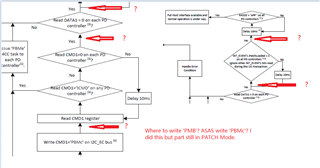
So, the address in the register table(2-1) are the register numbers(Table 1-1).

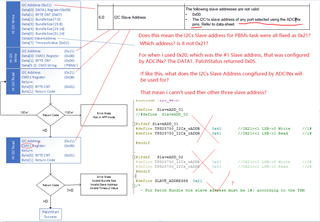
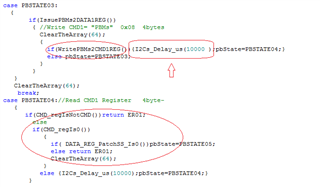
- The Engineer told me that it can take 1 of 4 I2C addresses, 0x20, 0x21, 0x22 or 0x23, as the slave address. But I found that it seems ignored the bit0(W/R)? For the bit0 cannot be sure from datasheet view, which decided by the actual condition.
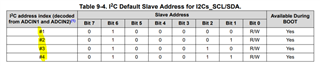
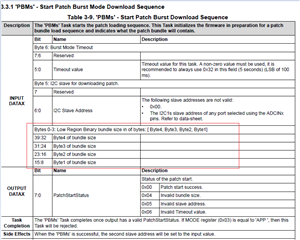
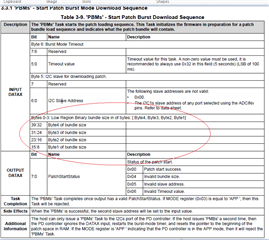
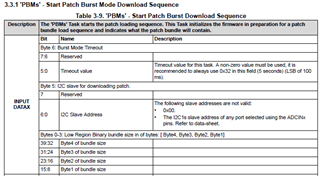
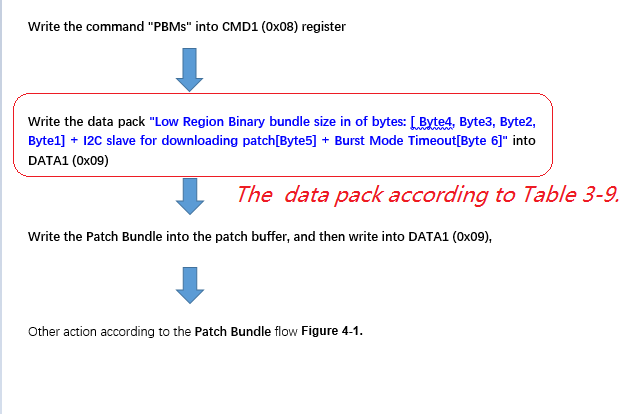
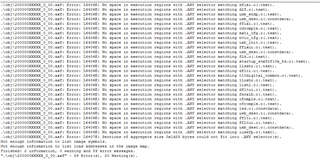
- The table below, where can be looked for? I cannot find in the datasheet and also the technical reference manual, but it's really important and necessary for developers.
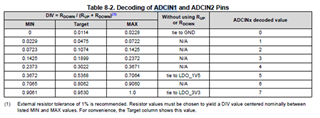
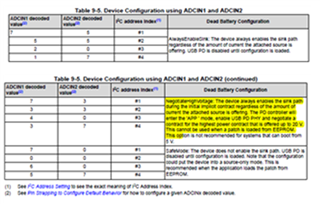
That's why I'm confused on the actual slave address, as well as the unique address. If have no these data, we really don't know how to configure, what’s the meaning of the decoded values, for there are 3 teams of configuration:
Thank you,
Franz