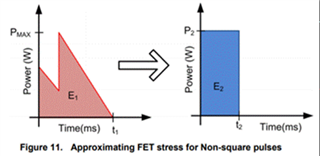
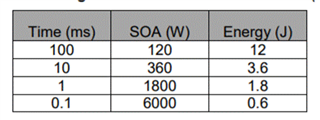
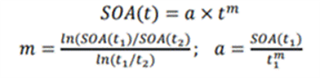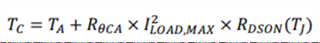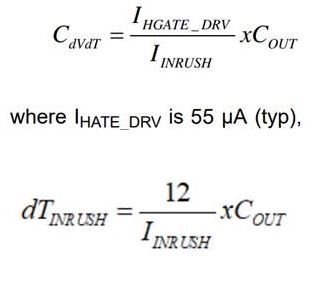Other Parts Discussed in Thread: LM25066, LM74800-Q1
Hi Team,
I use datasheet to calculate the CdVdT. The value is around 145nF. But customer only have 470nF in customer factory. Can you let me know if there is any potential risk that we place much higher cap for CdVdT?
Roy