Tool/software:
Hi TI Experts,
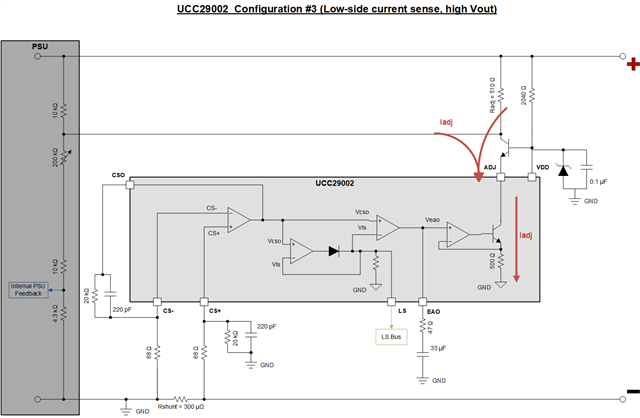
I'm designing a circuit to share the load equally among 4 boost converter outputs. Each boost converter is rated for 1500W and the output voltage is adjusted by the internal Rsense pot of the boost converter to 60V. I used the latest UC29002 Design Calculator to choose the values for the load share circuit (see the attached file). I chose Configuration 3 with low-side current sensing, keeping in consideration the high output voltage of the boost converter.
For Radj, I had to choose a value greater than 299 Ohms, so I set it to 510 ohms.
When I connect the load share circuit to the boost converter, with just a single converter, the output voltage drops from 60V to the value of the input voltage (24V). On investigating the boost converter circuit, I found that the connection of Radj to the boost converter causes it to come in parallel with the Rsense pot and this causes the feedback voltage to the boost converter circuit to increase. The attached file shows the simplified internal circuit of the feedback portion of the boost converter and its connection to the load share circuit. The Rsense pot is set to around 200K.
If I were to increase Radj beyond the value of the Rsense pot (to say 1Meg), I could keep the feedback voltage within range. However, this causes the compensation cap Ceao to increase to almost 3.8MF.
Let me know your thoughts on a possible solution.
Regards,
Mohan.
Boost-Converter+Load-Share.pdf
UCC29002_Design_Calculator_V1.1_17-9-24 - for 1500W boost converter.pdf