[ LMG3410 ] Optimal Dead Time
Hi,
Can you help me to understand the optimal dead time for half-bridge with LMG3410?
As my understanding, the too long dead time would cause power loss. On the other hand, of course, we need to prevent on-on state and shoot-through with appropriate dead time between two LMG3410s.
<Q1>:
Do you have any guide lines how to calculate valid dead time for half bridge with LMG3410?
I checked the user's guide of LMG34XX-BB-EVM, 50nS dead time interval is set. This dead time is applicable for switching frequency between 50KHz and 200KHz. Correct?
My customer's Fs is around 8KHz, in this case, any recommendation and/or limitation of dead time?
The current dead time which customer set is around 2uS.
<Q2>:
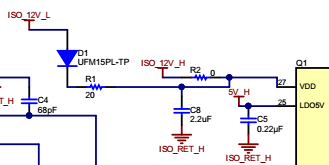
The LMG3410 datasheet says that...
"If a large deadtime is needed, a 14-V zener diode can be used in parallel with
the VDD bypass capacitor to prevent damaging the high-side LMG3410."
How can I know my dead time is large or small?
Thanks,
Ken
Reference
Deadtime Effect on GaN-Based Synchronous Boost Converter and Analytical Model for Optimal Deadtime Selection
ieeexplore.ieee.org/.../login.jsp
LMG5200 Simulation Dead Time V.S. Power Loss
e2e.ti.com/.../410260