Hi Team,
eg.
Since in the process of UART to simulate the Lin signal, the Lin signal needs a signal of >=13bit, UART cannot send 13-bit data at once, I try to achieve it by reducing the baud rate.
However, during implementation, the process of switching baud rates is time-consuming, resulting in the sent signal not being continuous, resulting in failure. The interface code used by Linux
static speed_t speed_arr[] = {B230400, B115200, B57600, B38400, B19200, B9600, B4800, B2400, B1200, B600, B300};
static int name_arr[] = { 230400, 115200, 57600, 38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, 600, 300};
static uint32_t uart_fd;
struct serial_t {
int fd;
char *device;/*/dev/ttyS0,...*/
int baud;
int databit;/*5,6,7,8*/
char parity;/*O,E,N*/
int stopbit;/*1,2*/
int startbit;/*1*/
struct termios options;
};
#define FILE "/dev/ttyS6"
static struct serial_t __seri_conf[] = {
[0] = {//connect with b board, ttyS6
.device = FILE,
.baud =9600,
.databit = 8,
.parity = 'N',
.stopbit = 1,
},
[1] = {//connect with b board, ttyS6
.device = FILE,
.baud =19200,
.databit = 8,
.parity = 'N',
.stopbit = 1,
},
};
/**
*@brief 设置串口通信速率
*@param fd 类型 int 打开串口的文件句柄
*@param speed 类型 int 串口速度
*@return void
*/
void set_speed(int fd, int speed)
{
int i;
int status;
struct termios Opt;
tcgetattr(fd, &Opt);
for ( i= 0; i < sizeof(speed_arr) / sizeof(int); i++)
{
if (speed == name_arr[i])
{
tcflush(fd, TCIOFLUSH);
cfsetispeed(&Opt, speed_arr[i]);
cfsetospeed(&Opt, speed_arr[i]);
status = tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &Opt);
if (status != 0)
perror("tcsetattr fd1");
return;
}
tcflush(fd,TCIOFLUSH);
}
}
//设置非标准波特率,比如13292
int serial_set_speci_baud(struct serial_t *tty,int baud)
{
struct serial_struct ss,ss_set;
tcgetattr(tty->fd,&tty->options);
cfsetispeed(&tty->options,B38400);
cfsetospeed(&tty->options,B38400);
tcflush(tty->fd,TCIFLUSH);/*handle unrecevie char*/
tcsetattr(tty->fd,TCSANOW,&tty->options);
if((ioctl(tty->fd,TIOCGSERIAL,&ss))<0){
printf("BAUD: error to get the serial_struct info:%s\n",strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
ss.flags = ASYNC_SPD_CUST;
ss.custom_divisor = ss.baud_base / baud;
printf("ss.custom_divisor = %d \r\n",ss.custom_divisor);
if((ioctl(tty->fd,TIOCSSERIAL,&ss))<0){
printf("BAUD: error to set serial_struct:%s\n",strerror(errno));
//return -2;
}
ioctl(tty->fd,TIOCGSERIAL,&ss_set);
printf("BAUD: success set baud to %d,custom_divisor=%d,baud_base=%d\n",
baud,ss_set.custom_divisor,ss_set.baud_base);
return 0;
}
/*get serial's current attribute*/
static int serial_get_attr(struct serial_t *tty)
{
if(tcgetattr(tty->fd,&tty->options) != 0){
printf("SERIAL: can't get serial's attribute\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
/*update serial's attrbute*/
static int serial_attr_update(struct serial_t *tty)
{
tcflush(tty->fd,TCIFLUSH);/*handle unrecevie char*/
if((tcsetattr(tty->fd,TCSANOW,&tty->options)) < 0){
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
static int serial_init_databit(struct serial_t *tty)
{
if(serial_get_attr(tty)<0)
return -1;
tty->options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
switch(tty->databit){
case 5: tty->options.c_cflag |= CS5;break;
case 6: tty->options.c_cflag |= CS6;break;
case 7: tty->options.c_cflag |= CS7;break;
case 8: tty->options.c_cflag |= CS8;break;
default:
printf("SERIAL: unsupported databit %d\n",tty->databit);
return -2;
}
if(serial_attr_update(tty) < 0)
return -3;
printf("SERIAL: set databit to %d\n",tty->databit);
return 0;
}
static int serial_init_parity(struct serial_t *tty)
{
if(serial_get_attr(tty)<0)
return -1;
/*ignore framing and parity error*/
tty->options.c_iflag = IGNPAR;
switch (tty->parity){
case 'n':
case 'N':
/* Clear parity enable */
tty->options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
/* Enable parity checking */
tty->options.c_iflag &= ~INPCK;
break;
case 'o':
case 'O':
/* 设置为奇校检*/
tty->options.c_cflag |= (PARODD|PARENB);
/* Disnable parity checking */
tty->options.c_iflag |= (INPCK|ISTRIP);
break;
case 'e':
case 'E':
/* Enable parity */
tty->options.c_cflag |= PARENB;
/* 转换为偶效验*/
tty->options.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
/* Disnable parity checking */
tty->options.c_iflag |= (INPCK|ISTRIP);
break;
default:
printf("SERIAL: unsupported parity %c\n",tty->parity);
return -2;
}
if(serial_attr_update(tty) < 0)
return -3;
printf("SERIAL: set parity to %c\n",tty->parity);
return 0;
}
static int serial_init_stopbit(struct serial_t *tty)
{
if(serial_get_attr(tty)<0)
return -1;
switch(tty->stopbit){
case 1:
tty->options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;break;
case 2:
tty->options.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;break;
default:
printf("SERIAL: unsupported stopbit %d\n",tty->stopbit);
return -2;
}
if(serial_attr_update(tty) < 0)
return -3;
printf("SERIAL: set stopbit to %d\n",tty->stopbit);
return 0;
}
static void uart_init(struct serial_t* seri_conf)
{
uart_fd = open(FILE, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NONBLOCK);
seri_conf->fd = uart_fd;
set_speed(seri_conf->fd,seri_conf->baud);
if(serial_init_databit(seri_conf)<0)
printf("serial_init_databit error\n");
if(serial_init_parity(seri_conf)<0)
printf("serial_init_parity error\n");
if(serial_init_stopbit(seri_conf)<0)
printf("serial_init_stopbit error\n");
//struct termios opt;
tcgetattr(seri_conf->fd,&seri_conf->options);
seri_conf->options.c_iflag &=~(BRKINT|ICRNL|INPCK|ISTRIP|IXON);
seri_conf->options.c_lflag &=~(ICANON|ECHO|ECHOE|ECHONL|ISIG|IEXTEN);
seri_conf->options.c_oflag &=~(OPOST);
if(tcsetattr(seri_conf->fd,TCSANOW,&seri_conf->options)!=0)
printf("error");
}
static int8_t BoardDiag_linSend(uint32_t fd, uint8_t *writeBuf,
uint32_t byteCount)
{
int8_t ret = 0;
ret = write(fd, (uint8_t *)&writeBuf[0], byteCount);
if(!ret)
{
close(fd);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
static int8_t BoardDiag_linReceive(uint32_t fd, uint8_t *readBuf,
uint8_t byteCount)
{
int8_t ret = 0;
ret = read(fd, (uint8_t *)&readBuf[0], byteCount);
if(!ret)
{
close(fd);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
typedef struct
{
uint8_t sync;
uint8_t pid;
uint8_t data[7];
uint8_t checksum;
}linData_t;
void Lin_SendBreak(void)
{
uint8_t breakfield1;
int8_t status = 0;
linData_t linMasterData;
//break
uart_init(&__seri_conf[0]);
breakfield1 = 0x00;//usigned char breakfield
BoardDiag_linSend(uart_fd, (uint8_t *)(&breakfield1),
sizeof(breakfield1));
close(uart_fd);
//重置波特率
uart_init(&__seri_conf[1]);
set_speed(uart_fd,19200);
linMasterData.sync = 0x55;
linMasterData.pid = 0xC1;//PID:0xC1 1100 0001 ID: 0x01
linMasterData.data[0] = 0x07;// 0000 0111
protectId = 0x01;
linMasterData.checksum = LIN_MakeChecksum(protectId,sizeof(linMasterData.data),(uint8_t *)(&linMasterData.data));
status = BoardDiag_linSend(uart_fd, (uint8_t *)(&linMasterData),
sizeof(linMasterData));
}
int main(void)
{
Lin_SendBreak();
close(uart_fd);
return 0;
}
Excuse me:
Question 1.Is it feasible to simulate the Lin signal via UART on TDA4?
If so, is there any better way to reduce the time-consuming problem of switching baud rates?
If not, what other good way to do it?
Question 2: I used the devmem2 tool to read the data of the UART4 address 0x02840000 register, but when I use the devmem2 tool to write the value to the register address 0x02840000.I indicate that the write was successful, but the value did not change when re-reading.
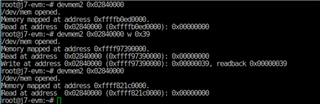
Does this register not allow modification?
Thanks,
Susan Ren

