Tool/software:
During the initialization of the hardware timestamp, the ioctl fails to write the hardware timestamp parameters. tx_type is HWTSTAMP_TX_ON, rx_filters is HWTSTAMP_FILTER_PTP_V2_EVENT. The following error occurs when the linuxPTP open source protocol stack v4.2 release is used, the following error occurs:
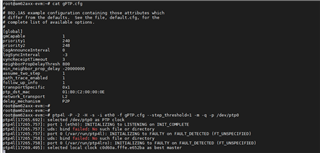
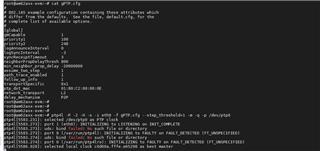
ptp4l[6.307]: selected /dev/ptp0 as PTP clock
ptp4l[6.364]: Setting HWTSTAMP: tx_type = 1, rx_filter = 12
ptp4l[6.364]: driver rejected most general HWTSTAMP filter
ptp4l[6.364]: Failed to set HWTSTAMP with rx_filter = 12: Invalid argument
ptp4l[6.364]: Retrying with alternative rx_filter = 9
ptp4l[6.364]: ioctl SIOCSHWTSTAMP failed: Invalid argument
ptp4l[6.416]: port 1 (eth0): INITIALIZING to FAULTY on FAULT_DETECTED (FT_UNSPECIFIED)
ptp4l[6.416]: port 0 (/var/run/ptp4l): INITIALIZING to LISTENING on INIT_COMPLETE
ptp4l[6.417]: port 0 (/var/run/ptp4lro): INITIALIZING to LISTENING on INIT_COMPLETE
The relevant code is as follows, sk.c/hwts_init
Time stamping parameters for eth0:
Capabilities:
hardware-transmit
software-transmit
hardware-receive
software-receive
software-system-clock
hardware-raw-clock
PTP Hardware Clock: 0
Hardware Transmit Timestamp Modes:
off
on
Hardware Receive Filter Modes:
none
ptpv2-l4-event
ptpv2-l4-sync
ptpv2-l4-delay-req
ptpv2-l2-event
ptpv2-l2-sync
ptpv2-l2-delay-req
ptpv2-event
ptpv2-sync
ptpv2-delay-req
driver: am65-cpsw-nuss
version: 6.6.32-ti-ge204a3987642
firmware-version:
expansion-rom-version:
bus-info: 8000000.ethernet
supports-statistics: yes
supports-test: no
supports-eeprom-access: no
supports-register-dump: yes
supports-priv-flags: yes
Based on the above information, can you tell me the failure information? I think the parameters set are within the support range