Tool/software:
Hello All
I have been working with our platform with OSPI interface and controlling a 256Mb SPI-NOR Quad device.
I have successfully initialsed the device with using the spi-cadence-quadspi driver as outlined in the Ti OSPI/QSPI guide:
I understand that the above link is for the 08.03.00.19 release but still outlines the driver that is required in the kernel to support quad spi.
I am using the current 10.01.10 release (6.6 kernel)
https://git.ti.com/cgit/ti-linux-kernel/ti-linux-kernel/snapshot/ti-linux-kernel-10.01.10.tar.gz
The spi and cadence kernel drivers are enabled:
CONFIG_SPI=y CONFIG_SPI_DEBUG=y CONFIG_SPI_MASTER=y CONFIG_SPI_MEM=y # # SPI Master Controller Drivers # CONFIG_SPI_BITBANG=y CONFIG_SPI_CADENCE_QUADSPI=y CONFIG_SPI_CADENCE_XSPI=y CONFIG_SPI_GPIO=y CONFIG_SPI_OMAP24XX=y # # SPI Protocol Masters # CONFIG_SPI_SPIDEV=m
And identifies the flash correctly when used as an mtd device:
[ 1.188137] cadence-qspi fc40000.spi: couldn't determine phase-detect-selector [ 1.190538] spi-nor spi0.0: xxxx25nw (32768 Kbytes)
spi-nor debug give correct information about the device:
$ cat /sys/kernel/debug/spi-nor/spi0.0/capabilities Supported read modes by the flashddir 1S-1S-1S opcode 0x13 mode cycles 0 dummy cycles 0 1S-4S-4S opcode 0xec mode cycles 2 dummy cycles 6 4S-4S-4S opcode 0xec mode cycles 2 dummy cycles 6 Supported page program modes by the flash 1S-1S-1S opcode 0x12 1S-4S-4S opcode 0x3e cat /sys/kernel/debug/spi-nor/spi0.0/params $ cat /sys/kernel/debug/spi-nor/spi0.0/params id xx xx xx 00 00 00 size 32.0 MiB write size 1 page size 256 address nbytes 4 flags 4B_OPCODES | HAS_4BAIT | HAS_16BIT_SR | SOFT_RESET opcodes read 0xec dummy cycles 8 erase 0xdc program 0x3e 8D extension invert protocols read 1S-4S-4S write 1S-4S-4S register 1S-1S-1S erase commands 21 (4.00 KiB) [1] ff (32.0 KiB) [2] dc (64.0 KiB) [3] c7 (32.0 MiB) sector map region (in hex) | erase mask | flags ------------------+------------+---------- 00000000-01ffffff | [ 123] |
Using flashrom I can dump the device without issue. Having some issues writing to the device but will put this on a different ticket as I dont think its linked to my spidev issue.
When I enable the ospi interface and set the flash device to be spidev compatible I get a /dev/spidev0.0 node but cannot do anything with the interface.
Working my way through the driver layers it seems to break in the spi_async operation returning an ENOTSUPP error code.
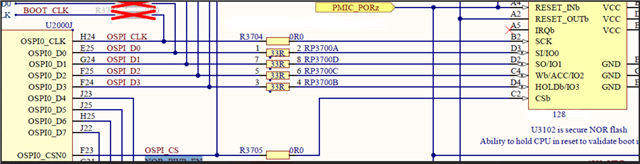
dts config:
&ospi0 {
bootph-all;
status = "okay";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&ospi0_pins_default>;
reg = <0x00 0x0fc40000 0x00 0x100>,
<0x05 0x00000000 0x01 0x2000000>;
flash@0 {
bootph-all;
compatible = "micron,spi-authenta";
reg = <0x0>;
spi-tx-bus-width = <1>;
spi-rx-bus-width = <1>;
spi-max-frequency = <20000000>;
cdns,tshsl-ns = <60>;
cdns,tsd2d-ns = <60>;
cdns,tchsh-ns = <60>;
cdns,tslch-ns = <60>;
cdns,read-delay = <4>;
};
};
I can get spidev to work with the single line interaces such as main_spi0, 1 and 2.
For some reason cannot get spidev to work with the ospi interface.
Is this possible?
I ask because our design requires the use of spidev for development.
Thank you for your assistance.
Marc