Tool/software:
Hello,
I am writing to inquire about the GPMC timing on the AM623.
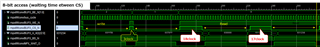
We are experiencing an issue with the read access on the GPMC, where the delay between two read accesses is significantly long, approximately 17-18 clock cycles.
In contrast, the delay between two write accesses is only 3 clock cycles, making the read access interval notably longer.
The GPMC is connected to an FPGA.

GPMC Settings
・GPMC and NOR Flash . Synchronous Single Read (GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0)
・DMA is not used
・CYCLE2CYCLEDELAY:1
・CYCLE2CYCLESAMECSEN:1
・CYCLE2CYCLEDIFFCSEN:1
・BUSTURNAROUND:1
Could you please provide information on the following three questions:
1. Is the delay time between two read accesses reasonable?
2. Is it possible to reduce the delay?
3. Will using DMA help in reducing the delay time between two read accesses?
Thank you for your assistance.
Best regards,
Eiji

