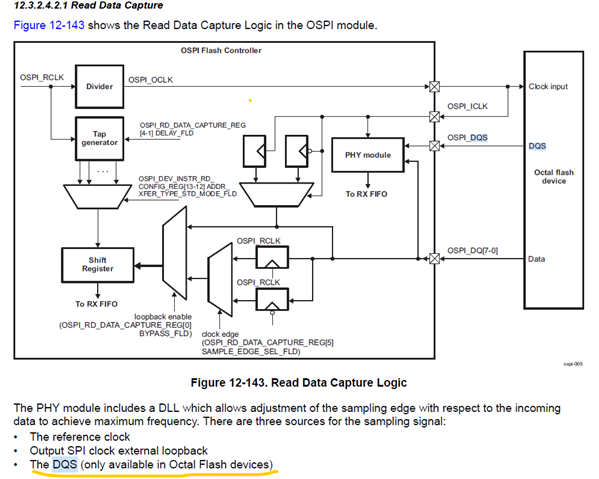
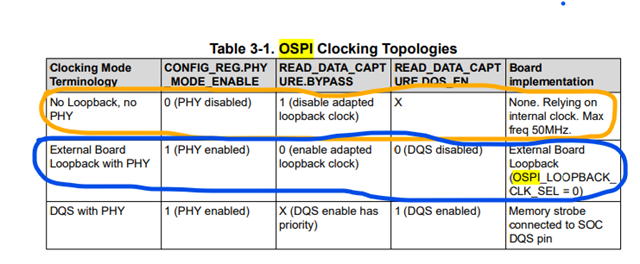
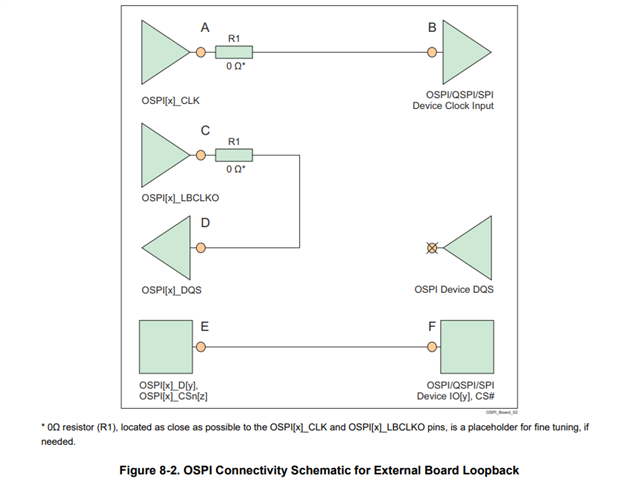
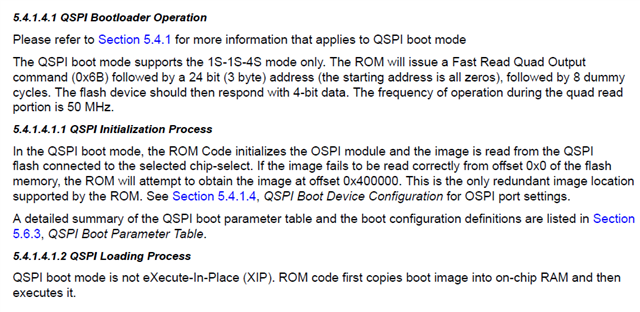
Tool/software:
Hi,
My customer will try to use QSPI boot (Not OSPI).
To confirm correct schematic, I'm checking schematic checklist tool as shown below.
https://www.ti.com/jp/lit/an/sprad91b/sprad91b.pdf
When I check spread sheet, there is following description.
According to this, when user use serial flash for boot, it seems that LBCLKO will be automatically driven as output.
This is defined in "OSPI" column, but is it applied to QSPI as well ?
What kind of output signal is observed on LBCLKO during booting ?
Best Regards,