Dear All,
We are currently working on the customized board. In the customized board we have to DSP C6678 processors. There are totaly (8cores for DSP1 + 8cores for DSP2)
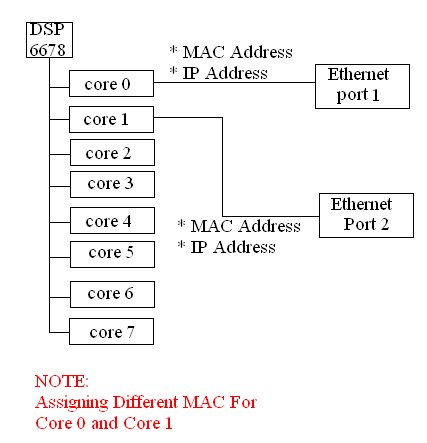
16 cores. In the customized board we have two ethernet port's. We are trying to enable ethernet port1 for core0 of DSP1 with a Seperate MAC Address and IP Address.
We are also trying to enable ethernet port2 for core1 of DSP1 with a Seperate MAC Address and IP Address.
The image given bellow clearly explain what I am trying to do.
1. How to assign 2 different MAC Address and 2 different IP Address for Core0 and Core1 of same DSP?
Regards,
Avinash N
Cornet Technology