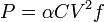Hello,
Relating to the C55xx_PowerSpreadsheet_RevB.xls (http://processors.wiki.ti.com/images/2/24/C55xx_PowerSpreadsheet_RevB.zip)
it seems that total CPU current is function of
* CPU Frequency (which is normal)
* CPU utilization (regarding from 100 % NOP to 100 % MAC )
I really do not undersand how the CMOS dynamic power consumption can be related to CPU utilization. From my comprehension, CPU clock is the same, whatever its utilization.
May some one give me some details ?
Thanks.
Nicolas