Hi,
My application, based on OMAP-L138, NO OS, requires USB Mass Storage support.
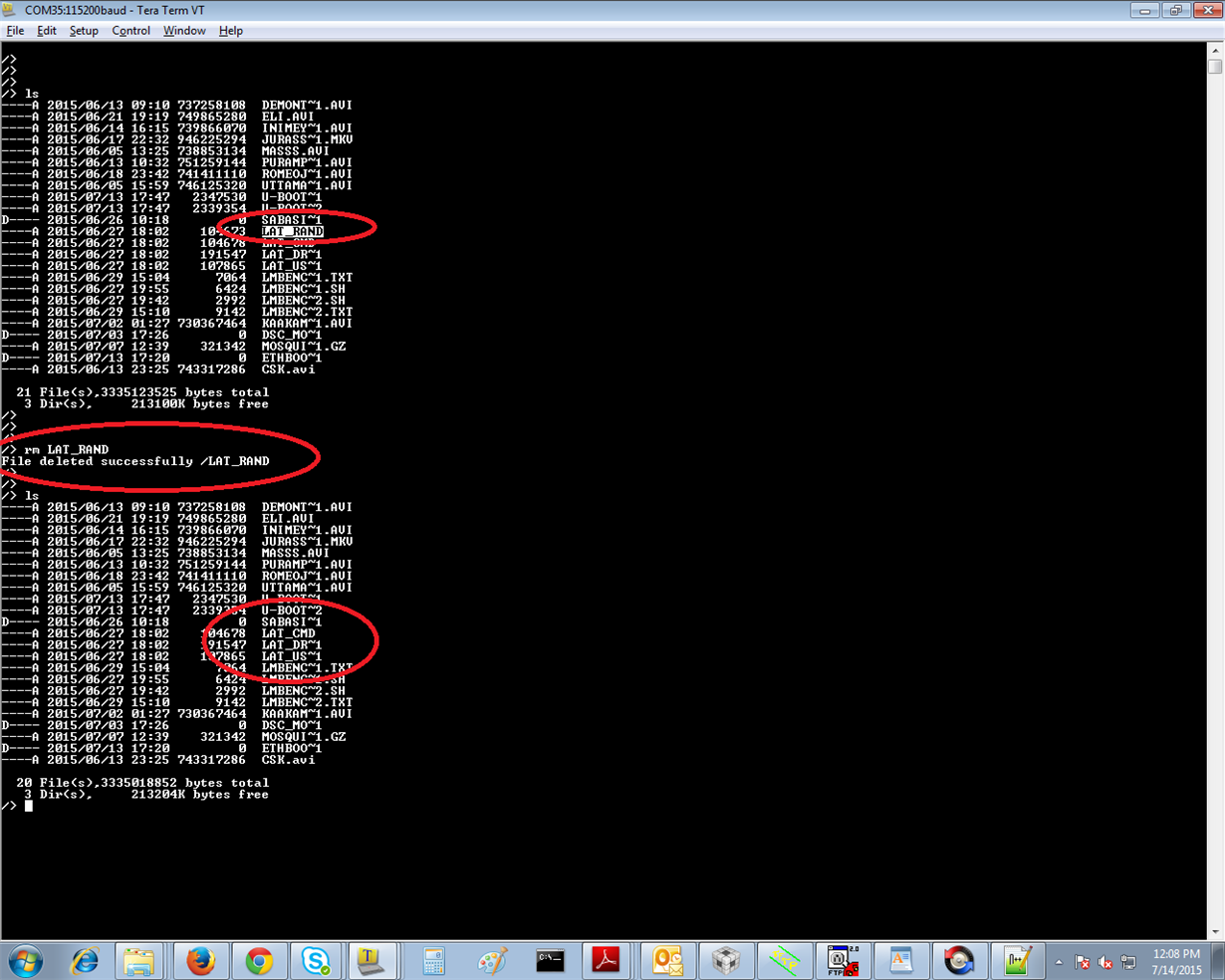
I need to store Log file in USB Mass Storage, and when USB near full, I have to delete older file.
There is no "DELETE" command in (OMAPL138_StarterWare_1_10_04_01\examples\lcdkOMAPL138\ usb_host_msc).
any help?
Guan