Hi,
For one of the Design Service Project Requirement, we are considering the TI's AM572x Sitara processor. Whether the following the feature are supported in AM572x HW and Linux BSP
- Boot Mode Requirement :
- SPI flash (with kernel and rootfs located in eMMC). This to be considered the normal, deployed case
- SPI flash (with kernel loaded via TFTP and NFS root file system)
- UART boot (Disaster recovery)
- Ethernet Requirement:
- Jumbo frame support
- IP/UDP/TCP checksum offloading
- Hardware buffer management
- How many Giga bit(1000Mbps) and 10/100 Mbps Ethernet port supported in various sub-systems(ARM, DSP, PRU-ICSS...)
- What is its performance parameter of all ethernet ports?
- Real-Time(RT) Patch: The Linux kernel used in the BSP is a Real-Time kernel, with RT patch applied
- If RT patch is applied in Linux Kernel, whether following performance can be achieved
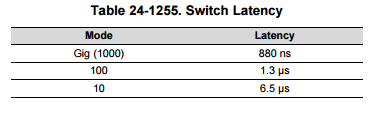
- Ethernet packet arrival jitter within 50us in user space
- Ethernet latency within 100us in user space
- Crypto Engine:
- Please provide more detailed documentation for Crypto Engine features and capabilities.
- Whether Linux BSP supports this feature?
- Will this be available as Library APIs for application development?
- PCIe:
- Number of Lanes supported in PCIe.
- Field Upgrade:
- Whether remote update of UBoot, Kernel and File system is supported in BSP
- And is it possible to upgrade through USB and Ethernet
Please provide your valuable inputs for each of the above requirement to use it in our design solution.
Thanks & Regards,
Madhu