Hi,
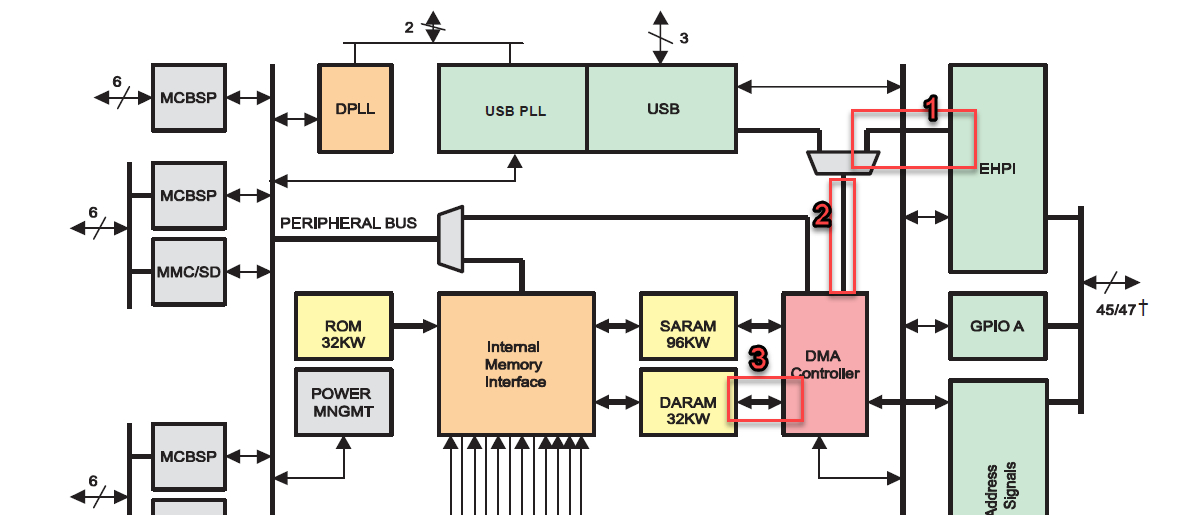
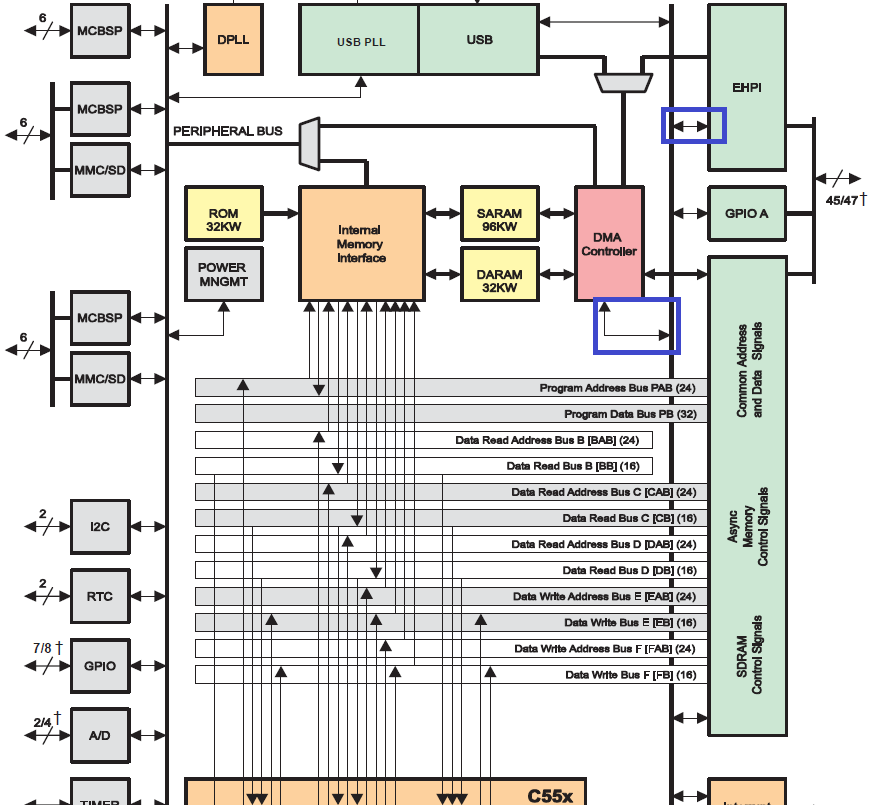
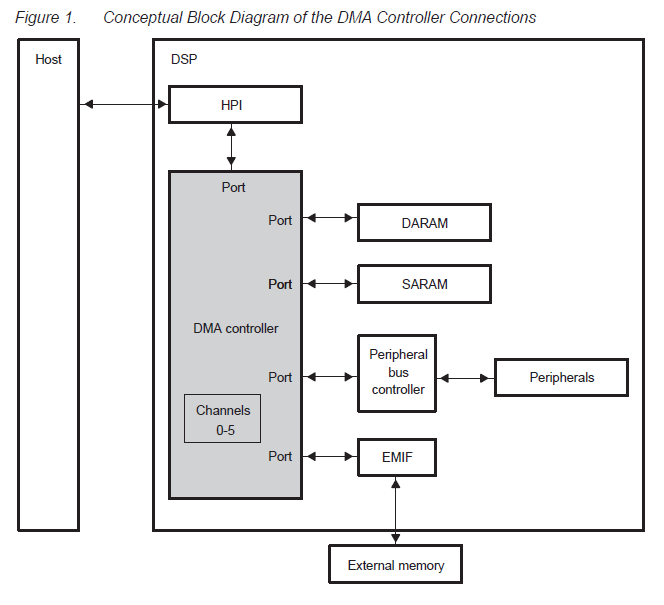
As you can find in the image below, I consider this path in order to access TMS320VC5509A's DARAM via HPI. Is there any different suggestion?
As you know, we can use another path with this order;
1-HPI to the peripheral bus
2-from the peripheral bus to the DMA controller
3-from DMA controller to DARAM.
But in my opinion, the first path shown in the image above is better because the peripheral bus might be busy for other applications. Does anyone have any other reason in his/her mind which could confirm my idea other than the one I mentioned?
Regards,
Hossein