Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TMS320VC5509A
Hello,
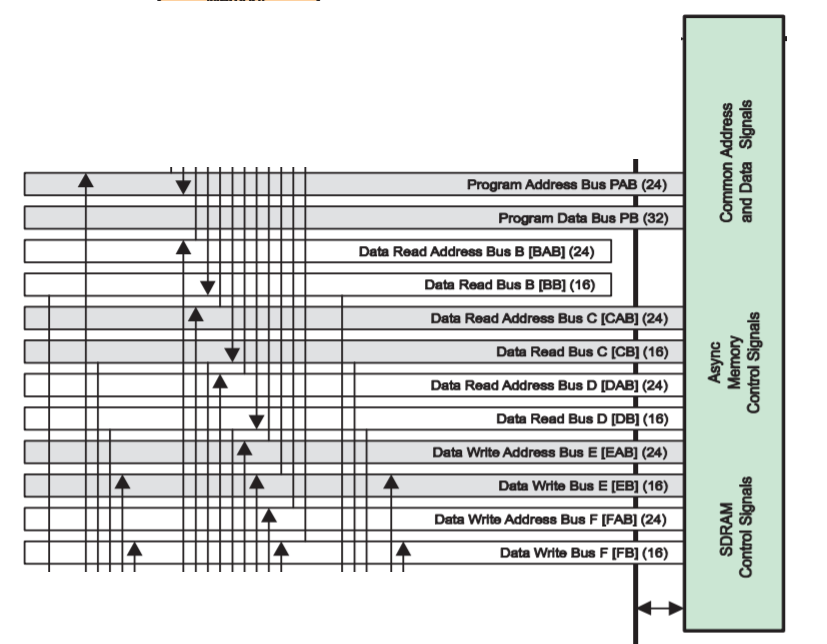
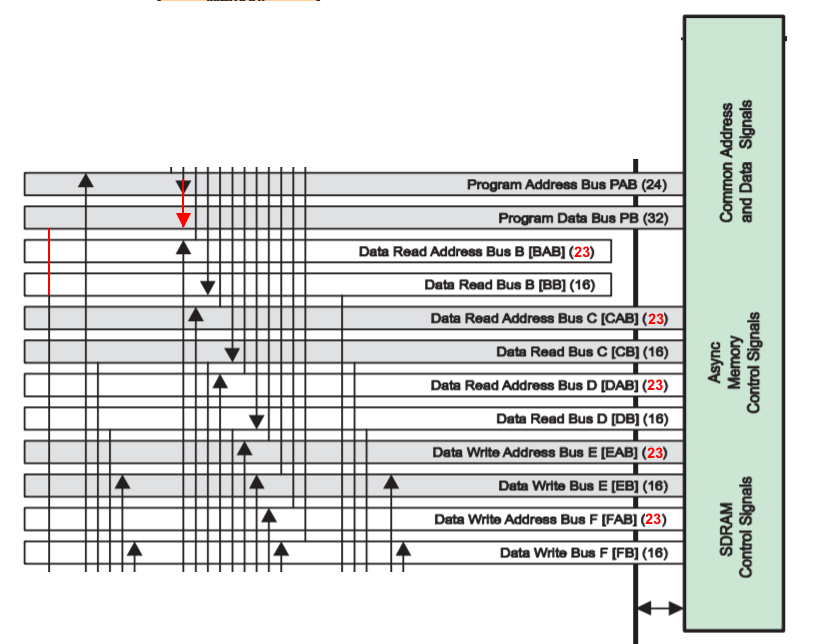
As you can see in the picture below the data (read/write) address busses are 24 bit wide, while from spru317f we know that these busses are 23-bit wide which is suitable for addressing 8 M*16-bit words of data.
So again I think this is another mistake in datasheets of TMS320VC5507 and TMS320VC5509A where the block digram of device is shown.
Regards,
Hossein