Other Parts Discussed in Thread: AWR6843, AWR1642, AWR1843, AWR2243
If you are already working on AWR1642/AWR1843/AWR6843 (1st gen) mmWave sensor device and wondering if to move to the AWR2944 (2nd Gen) mmWave Sensor then read further.
Here is high level feature difference b/w 1st Gen and 2nd Gen mmwave Sensor (from Datasheet)
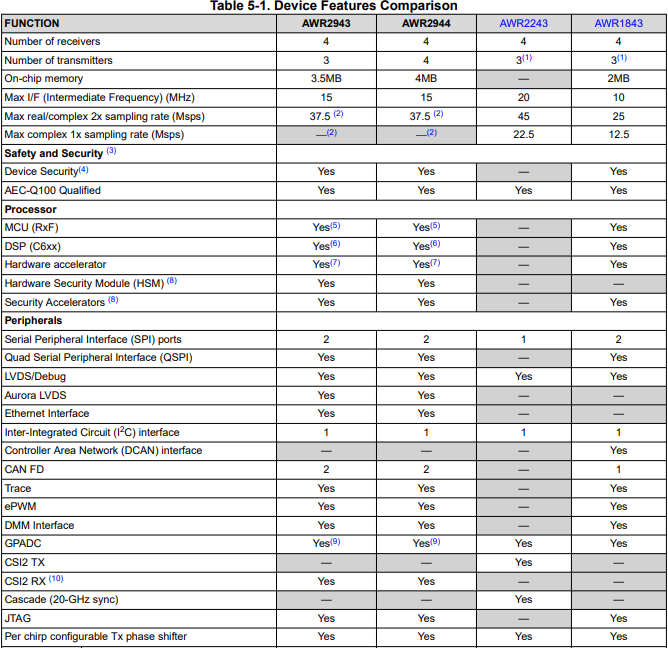
| Features | AWR2944 | AWR2243 | AWR1843 | AWR1642 |
| Max Range(m)* | 180-200 |
200-250 (single chip) 350+ (4xAWR2243 cascade) |
120-150 | 60-80 |
|
Beam forming/Steering (using Tx Phase Shifter) |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes | No |
| Usecase |
Corner Radar, Front Radar, ACC, AEB, FCW |
Front Radar, Corner Radar ACC(Adaptive Cruise Control) AEB (automated emergency Braking) AES (Autonomous Emergency Steering) FCW(Forward Collision Warning) |
ALC (Automtic Lane Change), BSD (blind spot detection) ACC, AEB, CTA (cross Traffic Alert), Parking, |
BSD, Parking, ALC, CTA |
NOTE: selection of mmWave Sensor is purely depends on your usecase and it's range/velocity/accuracy specification. Above range data based on TI EVM, device chirp/profile configuration and can be further improved using high gain antenna and processing chain. Refer this appNote to understand about object vs range https://www.ti.com/lit/an/swra593a/swra593a.pdf
Here usecase is small subset of all possible usecase with those devices, but user can extend that possibility with their application implementation.

