Other Parts Discussed in Thread: INA823
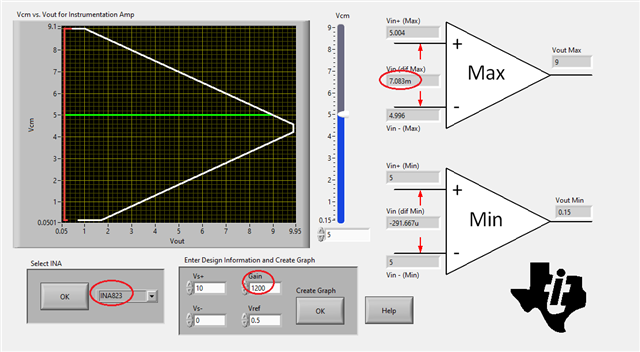
hello with the Demo board connect to a pressure sensor the INA output has a variation of +-7mv.
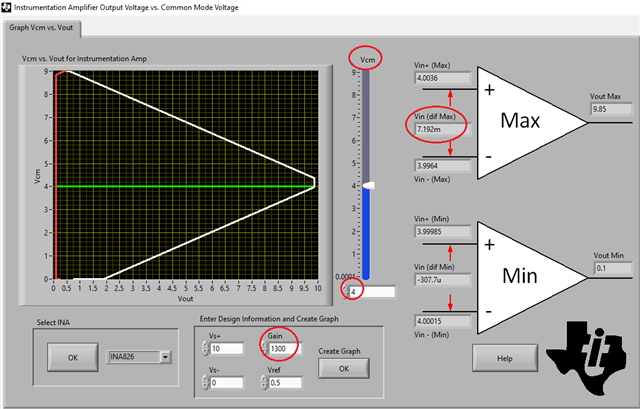
The 4" inch wire connects the PCBA to the sensor. based on what I measured, the 826 may not be appropriate for such a high gain.
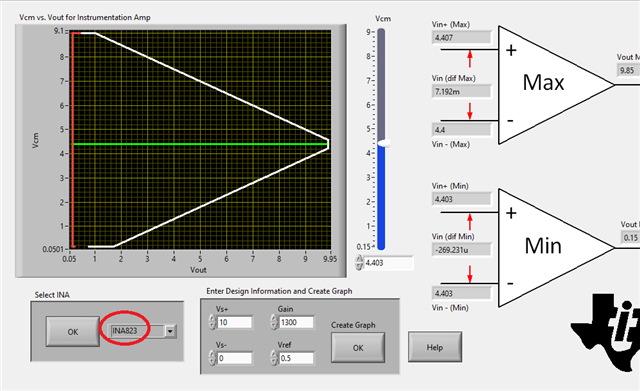
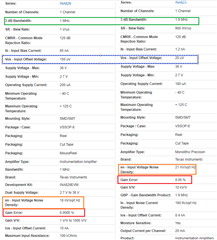
Would an 823 would be a better choice,
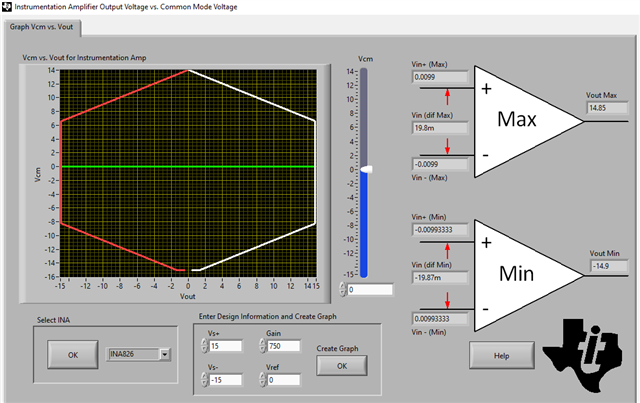
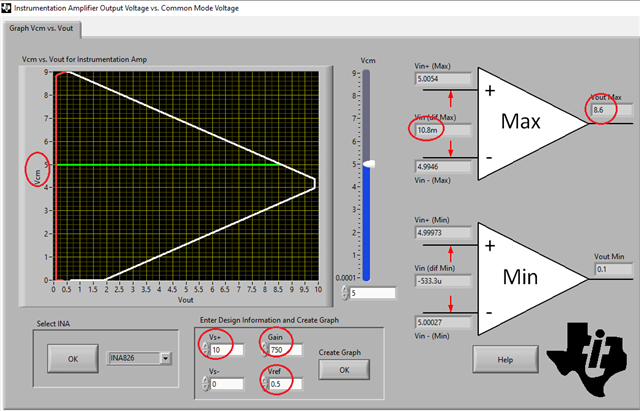
Spec: input is 5V CM with a gain 1.4v, excitation voltage 10V with an offset off .5V Gain ~750 output swing ~0- 5V
The 826 was chosen because of its rail-to-rail capabilities.