Hello dear forum,
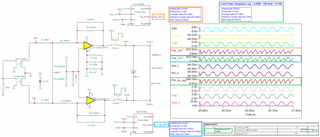
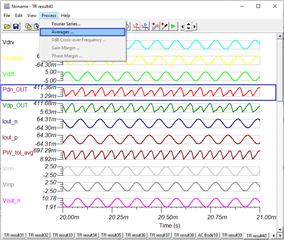
we are using in our application the ALM2402 to drive an load with approx. 100 Ohm impedance (1.5mHenry by 10Ohms DC resistance). The output of the amp is for both channels a sine wave with approx. 11.5 high peak and approx. 2V low peak, DC biased with approx. 6.7V - channel 2 same values just shifted at 180° degree. Both outputs are connected differentially to the load.
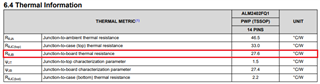
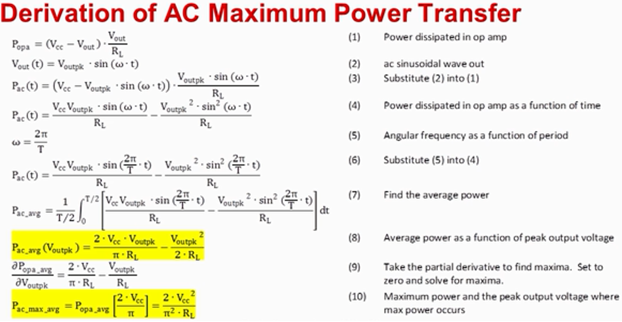
When I had a look to the datasheet (p.22), there is a formula to calculate power dissipation. I think the given formulas are dealing only the resistive load. Can you give me a hint how to calculate when a inductance is connected to the outputs ?
My plan is to calculate with the approach:
PAMP = PINSupply + (POUTSupply - PLOAD)
for PINSupply: VBAT * ICC of the IC
for POUTSupply: VBAT * ILOAD --> here i am not sure if the formula is correct, if I have to use the RMS or peak current.
for PLOAD: VOUTAMP * ILOAD * Cosi(Phi) --> Cos(Phi): cos(RDC/ZLoad) --> here i am not sure if the formula is correct, if I have to use single ended voltage or the differential voltage for VOUTAMP, and also not sure if i have to use the peak or RMS value, and for the current not sure if to use the peak or the RMS
After finishing the calculation should I calculate the results times 2, since there are two channels in the IC ? There is no hint/mention in the datasheet, regarding this question, I think this is calculated only for one channel.
This calculation, I assume deliver the average power loss. Can you give me an useful hint how to calculate the peak power instead of the average power ?
I found a DS of ALM2402 (maybe an old one): where the cos(phi) on the load is not considered, they used for the total calculation only the results from the formula: ALM2402-Q1 Dual Op-amp with High Current Output datasheet (Rev. D) (ti.com)
It would be gread if you can help.
BR and thanks in advance