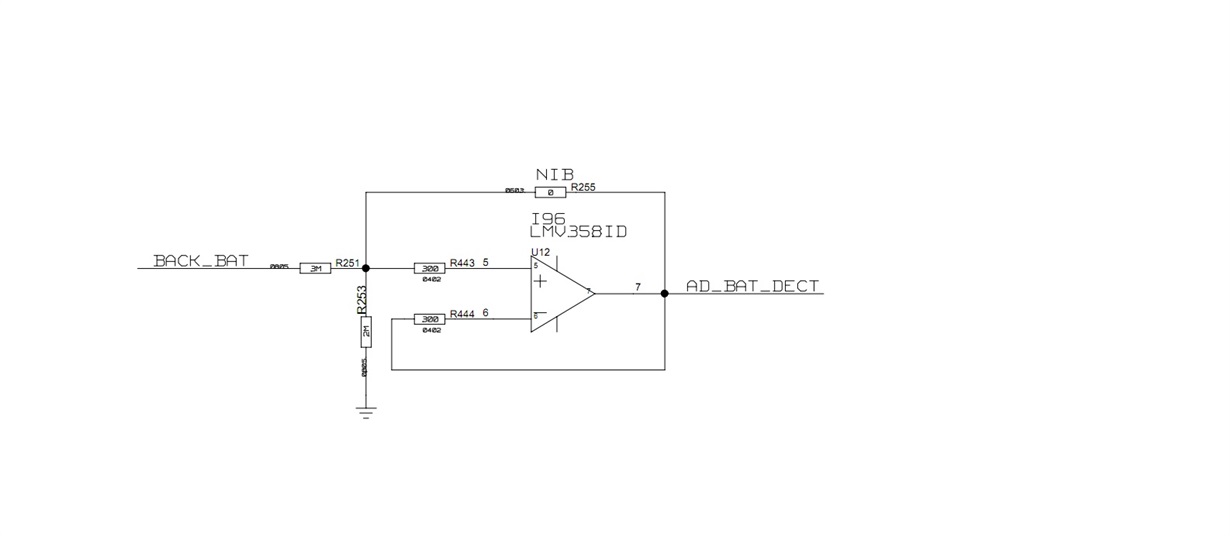
Hello,
My customer application is as below, they use scope to test the voltage between R251 and R443, they also test the pin7 voltage of our part, they find the voltage of pin7 is about 0.2V higher than input. Can you help to give your comment?
Regards,
Nanfang