Part Number: OPA544
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: OPA549, OPA548,
Good afternoon,
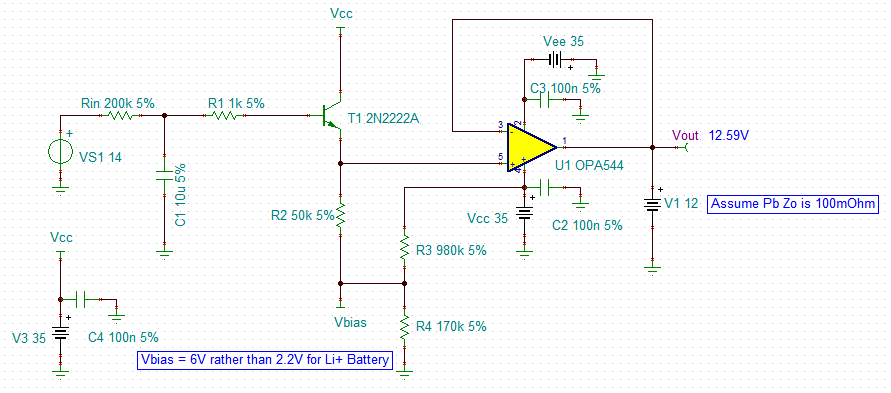
I have been looking at the document entitled, "Building Your Own Battery Simulator" (Application Report SLVA618–October 2013)
I would like to make use of this idea , but my requirement would be to simulate a Lead-Acid- chemistry battery of either 12 volts or 24 volts (two 12 volt batteries in series) .
As I don't need to simulate the internal protection of a Lithium Ion battery please explain how the circuit would need to be modified for lead acid.
Also, will this circuit work as is or is this just a very basic concept ? If so, would you be able to give more details about what might need to be added ?
Regards
Dave Whitaker