Hi TI expert,
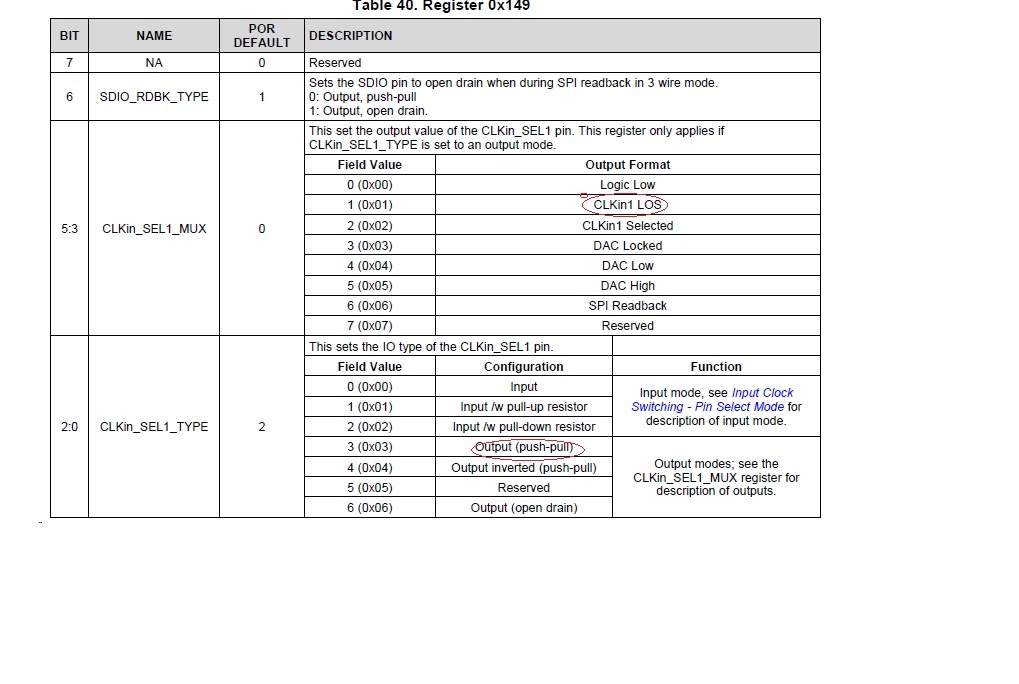
When we use the lmk04828, the clkin_sel0 and clkin_sel1 are configured to 0x1(CLKinX_LOS), the clkin_sel0_type
and he clkin_sel1_type are configured to output(push-pull ),
Are CLKin0_LOS and CLKin1_LOS refer to the loss of pll1 input refrence clk?
1: loss of input reference clk
0: input reference clk absence
Now, the clkin0 is 10MHz , clkin1 is not connected
But outputs of the pins of both clkin_sel0 and clkin_sel1 are low level.
Is this right?