Hello, I'm using tiva c series prototiping board, and pololu minIMU V. 3.0 with L3GD20H - LSM303D sensors, communicating to I2C0 Bus, I'm using sensorlib drivers in code but this alwais go to HardFault_Handler, i'm using Keil uvision 5.12 and TivaWare_C_Series-2.1.0.12573 libraries, mi code its divided in tre steps, first task code, second general driver (in this use tivaware functions) and third tivaware drivers,
code for mi task
__task void Posicion(void){
//Inicializacion del canal de datos I2C
CNFG_I2CM_Init();
//Inicializacion del sensor de Giroscopio
//L3GD20H_Init();
//Inicializacion del sensor de Acelerometro y Magnetometro
LSM303D_Init();
while(1){
while(velocista.ctrl_sys1 != 0){
//Lectura de datos de los sensores de posicion
L3GD20H_Gyr_Read(&velocista.Pos_Gyro[0], &velocista.Pos_Gyro[1], &velocista.Pos_Gyro[2]);
LSM303D_Acc_Read(&velocista.Pos_Accel[0], &velocista.Pos_Accel[1], &velocista.Pos_Accel[2]);
LSM303D_Mag_Read(&velocista.Pos_Mag[0], &velocista.Pos_Mag[1], &velocista.Pos_Mag[2]);
//Pausa del sistema
os_dly_wait (2);
}
//Pausa del sistema
os_dly_wait (2);
}
}
this is the code for my driver, this is based in sensorlib user guide
#include "rtl.h"
#include "stdbool.h"
#include "stdint.h"
#include "TM4C123GH6PM.h"
#include "hw_memmap.h"
#include "i2cm_drv.h"
#include "lsm303d.h"
#include "l3gd20h.h"
#include "hw_l3gd20h.h"
#include "hw_lsm303d.h"
#include "sysctl.h"
#include "i2c.h"
/*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Funciones requeridas para el funcionamiento del puerto I2C
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
// The I2C master driver instance data.
tI2CMInstance g_sI2CMSimpleInst;
// A boolean that is set when an I2C transaction is completed.
volatile bool g_bI2CMSimpleDone = true;
// The interrupt handler for the I2C module.
void I2CMSimpleIntHandler(void){
// Call the I2C master driver interrupt handler.
I2CMIntHandler(&g_sI2CMSimpleInst);
}
// The function that is provided by this example as a callback when I2C
// transactions have completed.
void I2CMSimpleCallback(void *pvData, uint_fast8_t ui8Status){
// See if an error occurred.
if(ui8Status != I2CM_STATUS_SUCCESS){
// An error occurred, so handle it here if required.
}
// Indicate that the I2C transaction has completed.
g_bI2CMSimpleDone = true;
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Funcion 1 'CNFG_I2CM_Init' Configuracion de transmision por puerto I2C
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void CNFG_I2CM_Init(void){
// The I2C master driver instance data.
tI2CMInstance g_sI2CMSimpleInst;
// A boolean that is set when an I2C transaction is completed.
//volatile bool g_bI2CMSimpleDone = true;
// Set the clocking to run directly from the external crystal/oscillator.
// TODO: The SYSCTL_XTAL_ value must be changed to match the value of the
// crystal on your board.
SysCtlClockSet(SYSCTL_SYSDIV_10 | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN |
SYSCTL_XTAL_16MHZ);
// Enable and initialize the I2C0 master module. Use the system clock for
// the I2C0 module. // I2C data transfer rate set to 400kbps.
I2CMasterInitExpClk(I2C0_BASE, SysCtlClockGet(), true);
//clear I2C FIFOs
//HWREG(I2C0_BASE + I2C_O_FIFOCTL) = 80008000;
// Initialize the I2C master driver. It is assumed that the I2C module has
// already been enabled and the I2C pins have been configured.
I2CMInit(&g_sI2CMSimpleInst, I2C0_BASE, INT_I2C0, 0xff, 0xff, 120000000);
}
///*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Funciones requeridas para el funcionamiento del sensor L3GD20H
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
// A boolean that is set when a L3GD20H command has completed.
volatile bool g_bl3gd20hDone;
// The function that is provided by this example as a callback when L3GD20H
// transactions have completed.
void l3gd20hCallback(void *pvCallbackData, uint_fast8_t ui8Status){
// See if an error occurred.
if(ui8Status != I2CM_STATUS_SUCCESS){
// An error occurred, so handle it here if required.
}
// Indicate that the L3GD20H transaction has completed.
g_bl3gd20hDone = true;
}
///*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Funcion 2 'L3GD20H_Init' Iniciaizacion del Giroscopio L3GD20H
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void L3GD20H_Init(void){
//float fGyro[3];
tI2CMInstance sI2CInst;
tL3GD20H sl3gd20h;
// Initialize the L3GD20H. This code assumes that the I2C master instance
// has already been initialized.
g_bl3gd20hDone = false;
L3GD20HInit(&sl3gd20h, &sI2CInst, 0x68, l3gd20hCallback, 0);
while(!g_bl3gd20hDone){
}
// Configure the L3GD20H for 500 deg/sec sensitivity
g_bl3gd20hDone = false;
L3GD20HReadModifyWrite(&sl3gd20h, L3GD20H_O_CTRL4, ~L3GD20H_CTRL4_FS_M, L3GD20H_CTRL4_FS_500DPS, l3gd20hCallback, 0);
while(!g_bl3gd20hDone){
}
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Funcion 3 'L3GD20H_Read' Lectura de datos del Giroscopio L3GD20H
*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void L3GD20H_Gyr_Read(float* fGyro_X, float* fGyro_Y, float* fGyro_Z){
// A boolean that is set when a L3GD20H command has completed.
volatile bool g_bl3gd20hDone;
float fGyro[3];
tL3GD20H sl3gd20h;
// Request another reading from the L3GD20H.
g_bl3gd20hDone = false;
L3GD20HDataRead(&sl3gd20h, l3gd20hCallback, 0);
while(!g_bl3gd20hDone){
}
// Get the new gyroscope readings.
L3GD20HDataGyroGetFloat(&sl3gd20h, &fGyro[0], &fGyro[1], &fGyro[2]);
// Return Gyroscope values in poiter
*fGyro_X = fGyro[0];
*fGyro_Y = fGyro[1];
*fGyro_Z = fGyro[2];
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Funciones requeridas para el funcionamiento del sensor LSM303D
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
// A boolean that is set when a LSM303D command has completed.
volatile bool g_bLSM303DDone;
// The function that is provided by this example as a callback when LSM303D
// transactions have completed.
void LSM303DCallback(void *pvCallbackData, uint_fast8_t ui8Status){
// See if an error occurred.
if(ui8Status != I2CM_STATUS_SUCCESS){
// An error occurred, so handle it here if required.
}
// Indicate that the LSM303D transaction has completed.
g_bLSM303DDone = true;
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Funcion 4 'LSM303D_Init' Iniciaizacion del Acelerometro y Magnetometro LSM303D
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void LSM303D_Init(void){
// A boolean that is set when a LSM303D command has completed.
volatile bool g_bLSM303DDone;
tI2CMInstance sI2CInst;
tLSM303D sLSM303D;
// Initialize the LSM303D. This code assumes that the I2C master instance
// has already been initialized.
g_bLSM303DDone = false;
LSM303DInit(&sLSM303D, &sI2CInst, 0x68, LSM303DCallback, 0);
while(!g_bLSM303DDone){
}
// Configure the LSM303D for +/- 4 g accelerometer range.
g_bLSM303DDone = false;
LSM303DReadModifyWrite(&sLSM303D, LSM303D_O_CTRL2,~LSM303D_CTRL2_AFS_M, LSM303D_CTRL2_AFS_4G, LSM303DCallback,0);
while(!g_bLSM303DDone){
}
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Funcion 3 'LSM303D_Acc_Read' Lectura de datos del Acelerometro LSM303D
*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void LSM303D_Acc_Read(float* fAccel_X, float* fAccel_Y, float* fAccel_Z){
// A boolean that is set when a LSM303D command has completed.
volatile bool g_bLSM303DDone;
float fAccel[3];
tLSM303D sLSM303D;
// Request another reading from the LSM303D.
g_bLSM303DDone = false;
LSM303DDataRead(&sLSM303D, LSM303DCallback, 0);
while(!g_bLSM303DDone){
}
// Get the new accelerometer readings.
LSM303DDataAccelGetFloat(&sLSM303D, &fAccel[0], &fAccel[1], &fAccel[2]);
// Return accelerometer values in poiter
*fAccel_X = fAccel[0];
*fAccel_Y = fAccel[1];
*fAccel_Z = fAccel[2];
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Funcion 4 'LSM303D_Mag_Read' Lectura de datos del Magnetometro LSM303D
*--------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void LSM303D_Mag_Read(float* fMag_X, float* fMag_Y, float* fMag_Z){
// A boolean that is set when a LSM303D command has completed.
volatile bool g_bLSM303DDone;
float fMag[3];
tLSM303D sLSM303D;
// Request another reading from the LSM303D.
g_bLSM303DDone = false;
LSM303DDataRead(&sLSM303D, LSM303DCallback, 0);
while(!g_bLSM303DDone){
}
// Get the new magnetometer readings.
LSM303DDataMagnetoGetFloat(&sLSM303D, &fMag[0], &fMag[1], &fMag[2]);
//
// Return accelerometer values in poiter
*fMag_X = fMag[0];
*fMag_Y = fMag[1];
*fMag_Z = fMag[2];
}
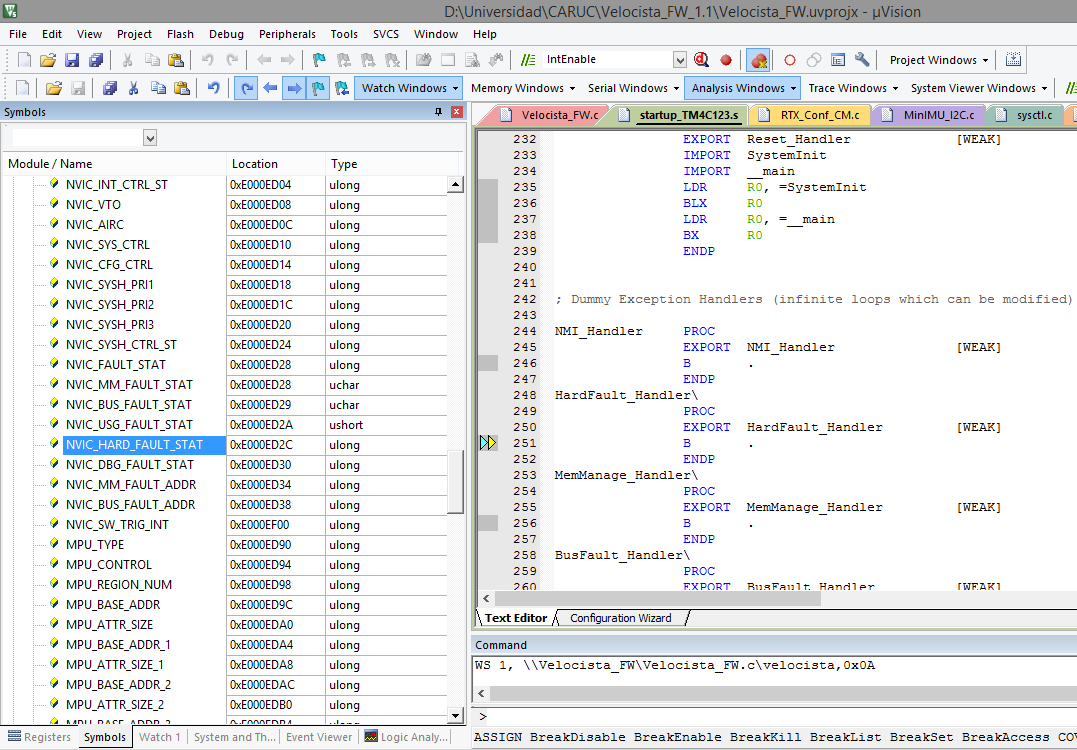
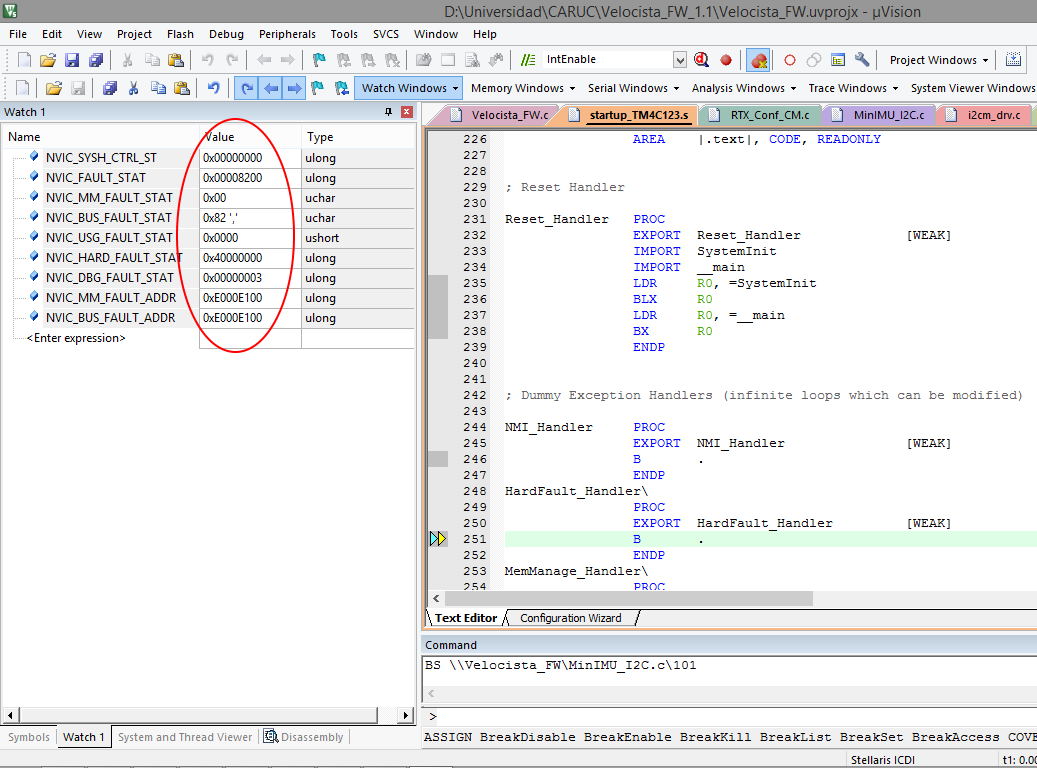
finali in debug i'm detect the code that generate the hardfault esception
in line:
I2CMInit(&g_sI2CMSimpleInst, I2C0_BASE, INT_I2C0, 0xff, 0xff, 120000000);
function go to enable interrupt in file i2cm_drv.c
MAP_IntEnable(ui8Int);
and finaly execute this code in interrupt.c
//
// Enable the general interrupt.
//
HWREG(g_pui32EnRegs[(ui32Interrupt - 16) / 32]) =
1 << ((ui32Interrupt - 16) & 31);
and go to hardfault exception
and the rebuild not generate errors
Thanks for your help !!