Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TIDM-3OUTSMTSTRP, , MSP-ISO, UNIFLASH, MSP430F67791, MSP430G2553
Hi.
My name Dung.
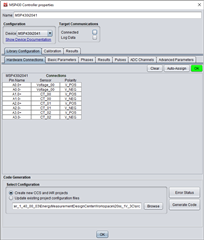
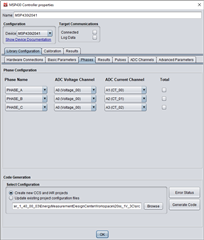
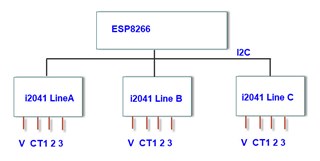
I have project with MSP430i2041 EVM 1 Voltage (990K-2.4K - 220VAC max 250V), 3 Current (CT 1000.1, R = 6.8R max 80A), my design the same TIDM-3OUTSMTSTRP and use CT, not include Relay.
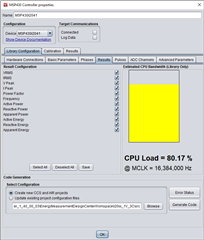
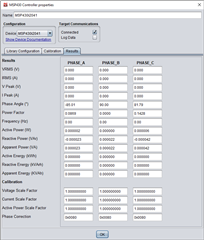
I have some question. On the EMDC when creat project why TI calculator approximately real value.
When I calib for MSP430i2041 by EMDC use KIT MSP430F5529LP, if only connect 3 CT to EVM, can read result to EMDC, when I connect 1V 3C to EVM it cannot connect to EMDC. I don't know why (I don't use MSP-ISO).