Hi TI experts,
I have a question about UCC28700.
1. Why the VDD connect to VBLK and Vaux. what's Vcc power up sequence?
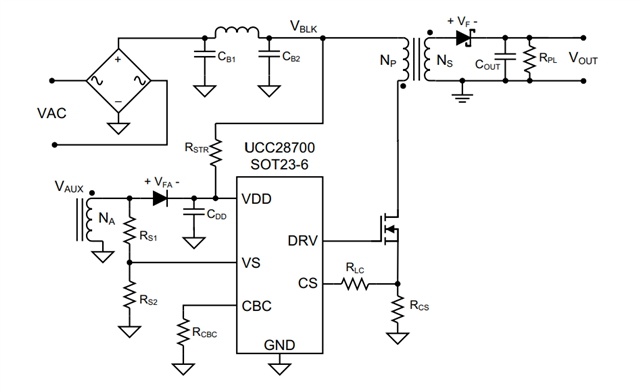
2. Why we need to use this diode? what's the function of this diode? can we remove it?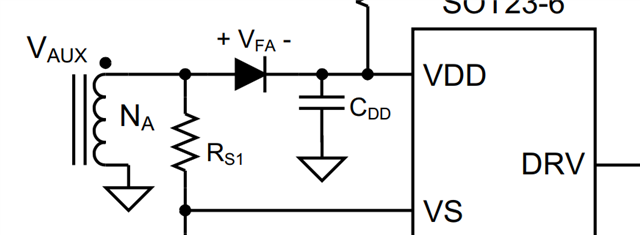
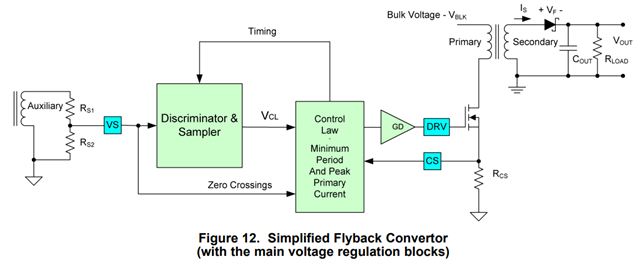
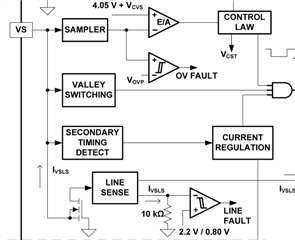
3.What is discriminator and sampler? is this made by analog or digital circuit?