Hi I'm Jieun,
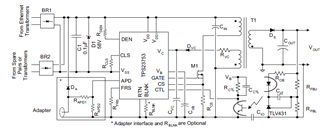
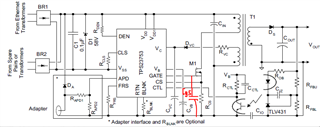
I have a question about Power dissipation of TPS23753A
When 48V POE voltage is applied to VDD pin, how can I calculate the power dissipation?
Also, I would like to know the same, when DC 12V aux adapter voltage is applied to VDD1 pin
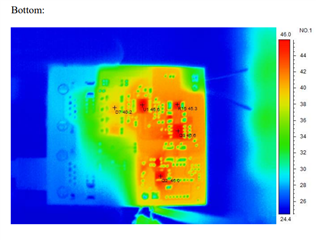
Power dissipation of TPS23753A when the power is applied
1) 48V POE
2) DC 12V aux
best regards,