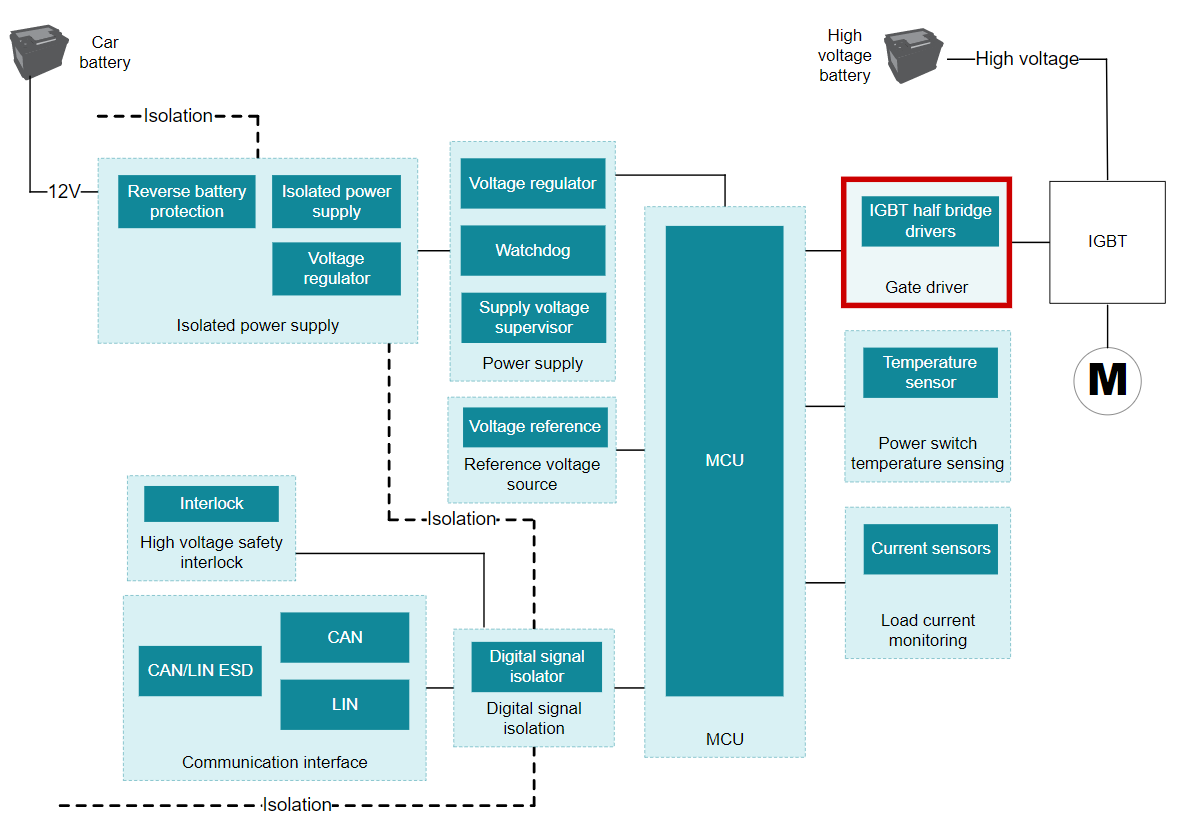
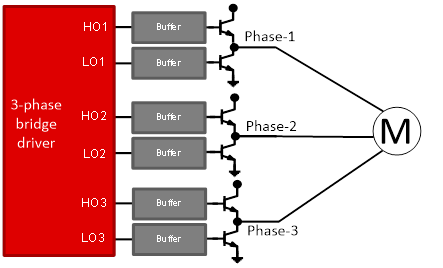
I am currently using 3-phase bridge drivers for the IGBTs of the inverter stage of a BLDC motor.
Why should I consider a gate driver to replace the 3-phase bridge driver in my existing solution? What are some performance advantages of the half-bridge gate drivers over my current solution?