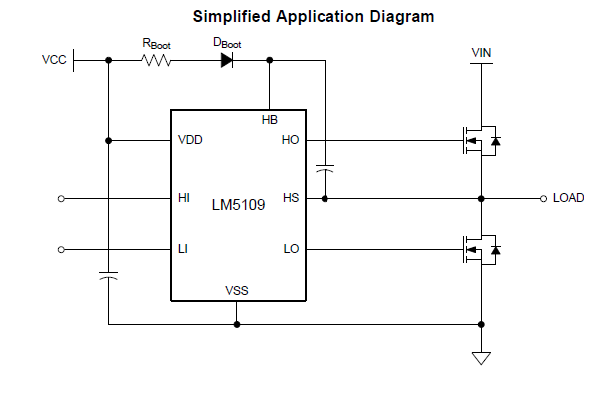
Hi,
I'm using this gate driver to control a half bridge contains two N-MOSFET, my MOSFET is powered by 36V, so my HO should be at least 46V to totally turn the MOSFET at on state, besides, my LO should be 12V. I don't understand the relationship of the input signal and the output signal. I'm wondering how to control the output voltage to get a desired voltage we need.