Other Parts Discussed in Thread: SYSBIOS, TEST2
Tool/software: TI-RTOS
Hi, I am porting some code from TI-RTOS PSDK4.1 to PSDK5.1.
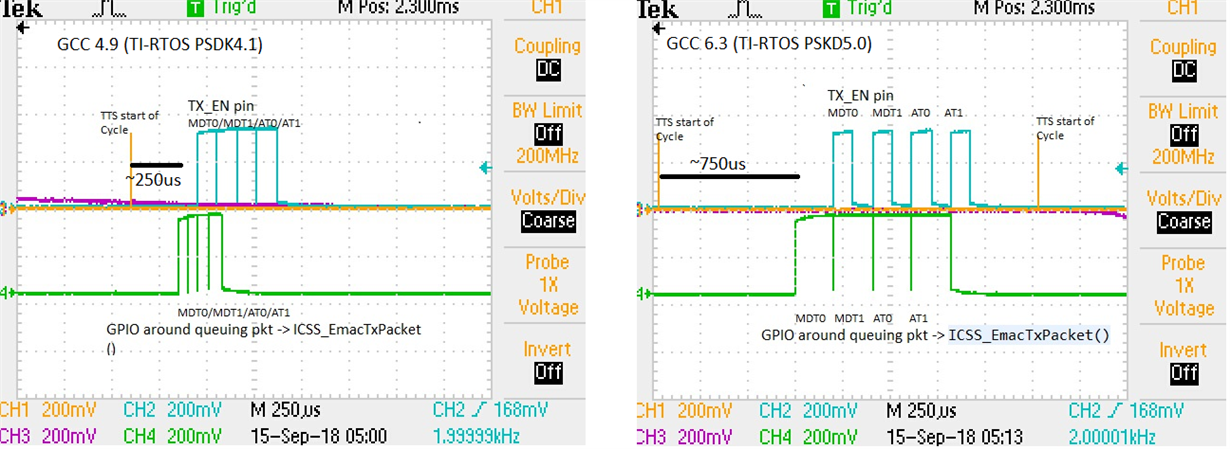
I noticed some functions were taking longer and happening later in time.. In other words, things seems to be slower. I originally thought this could be related to PDK changes, as the function I am profiling happens inside PRU-ICSS EMAC LLD. However, because I also see the function happening later, I am wondering if this is more related to newer GCC toolchain.
As a test, I tried to compile my code with PDK 1.0.9 (or later) and GCC4.9.3. In order to rule out (or confirm) GCC or PDK version issues. However, I hit so many error. It is really difficult to build with tools from a PDK4.2 (or greater) and GCC4.9.3.. so many changes..
For TI employs, who want to see more details there is a JIRA
My questions:
- Is it any known issue between these two GCC toolchains?
- I found a similar E2E. Here this user pointed out could be due to heap size. I am not sure, but in a simple program EMAC loopback is difficult to notice this, but in my program (much bigger) it is easy. Any suggestions?
- Any way we can rule out GCC version?. Just FYI, my current error when building with GCC4.9 and PSDK4.2 tools is "undefined reference to `clock_gettime'"
- Attaching a couple of scope snapshots to illustrate the issue.
Thanks in advace for your help
Paula