- Ask a related questionWhat is a related question?A related question is a question created from another question. When the related question is created, it will be automatically linked to the original question.
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
Dear, All
In the customer, it experimented about operation when the noise went into STB pin of SN65HVDA1040A-Q1.
The pulse of 100nS is added to STB pin using a pulse generator.
At this time, although the LIN bus was recessive as follows, RXD outputted the low pulse.
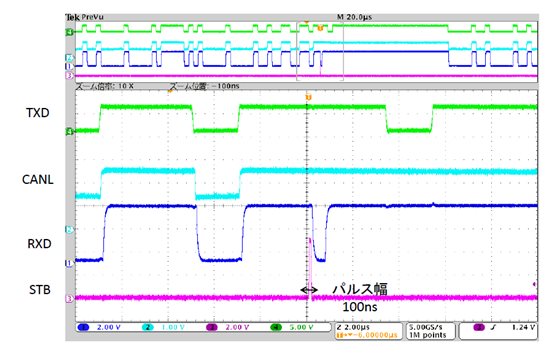
May this consider the malfunction for the pulse width of STB pin being too short?
Moreover, please let me know the minimum required pulse width about STB pin in this case.
Thanks, Masami M.
Hi Masami,
I have a few questions about your set-up to try and learn more:
I beleive what you are seeing is the delay from the device switching from one receive path to another. Inside the device there are two receive paths, a low power receive path, and a high power receive path that is unpowered in standby mode.
When the device switches modes, the signal to the RXD pin is switched through a mux between the two receive paths and if they both are not at the same logical value, then a glitch will be seen when switching.
Thanks,
John
Hi, John
Thank you for your reply.
> -Could you share a schematic?
The following figure is schematic of a test circuit.
> -Is the CANH bus line in any fault condition?
Or is it tied to CANLwith two terminationsofa 120 ohms resistance?(I understand you only have 4 channels on the scope, just want to make sure I am not missing a critical part of the set-up)
Please refer to schematic.
62-ohm two series connection is arranged to two places between CANL and CANH.
> -What temperature and voltage are you operating at?
Temperature is 25℃ ±5℃, and power supply voltage is 4.97V.
The following figure is a waveform of ①TXD, ②RXD and ③CANH-CANL, and ④STB.
③ is using the differential probe.
Thanks, Masami M.
Hi Masami,
I went into the lab this morning and ran your test on three different CAN devices that we offer.
The first thing I did was test the SN65HVDA1040A-Q1 device. I verified that I was able to see the glitch on RXD when a 100ns pulse was sent on STB pin.
I then tested the next family of transceives that we have, the SN65HVDA54x. This family does not have the SPLIT pin but has standby mode with bus wake up (like the SN65HVDA1040A-Q1). The two devices most functionally similar would be the SN65HVDA541-Q1 and teh SN65HVDA541-5-Q1 (does not have a VIO level shifting pin). This devices implements a short delay before switching from high power to low power receivers, and I verified that it does not have a glitch on the RXD pin when a 100ns pulse is sent on the STB pin. See below:
Lastly, I tested the latest family of CAN devices that we have, the HVDA553-Q1 (which is pin to pin replacement of the SN65HVDA1040A-Q1). I verified that it also does not have a glitch on the RXD pin when a 100ns pulse occurs on STB. See picture below:
I do not foresee the SN65HVDA1040A-Q1 device being redesigned, but there are two other options in our portfolio that could work for you if this is an issue. Please let me know if you have any other questions.
Thanks,
John
Hi, John
Thank you for the reply.
HDVA553-Q1 is introduced to a customer.
However, the customer is examining how to keep from taking out short STB with the program on the DSP side.
In this case, although necessity has the High Level time of the minimum STB, can't it show?
(for example, more than 2micro S)
Thanks, Masami M.
Hi Masami,
Great question. I should have included this in my first response. Please see the pictures below I captured with the SN65HVDA1040A-Q1 with different STB pulse widths.
STB tPULSE = 600ns
STB tPULSE = 650ns
STB tPULSE = 700ns
The very small ripple remains the same for gltiches of longer duration. Another example i took showing this is at STB tPULSE = 1000ns.
Therefore, I found a typical value at nominal temp and voltage to be a pulse of at least 700ns for the hard pulse down glitch to go away on the RXD pin.
Thanks,
John
Hi, John
Thank you for your reply.
I answer it to a customer.
Thanks, Masami M.