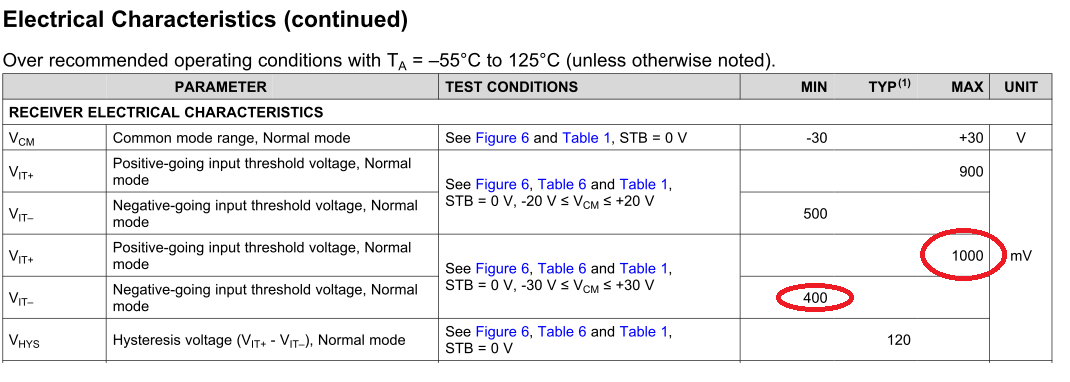
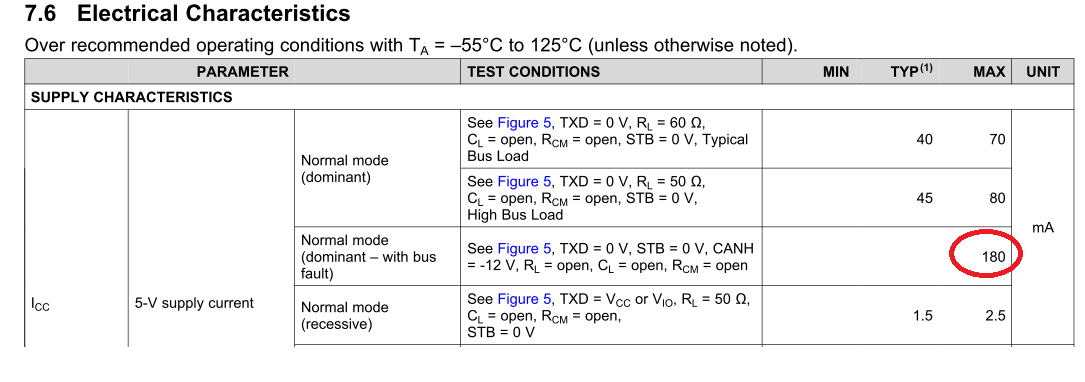
Hi,
My customer is wondering how to measure the reflection and if there are appnotes discuss about how the calculate or analysis.
They are now currently using 3 termination in the network but operating ok.
From my understanding the mainly concern should be the differential voltage cross load and the reflection problem.
Will it be ok to work with 3 termination resistor in the same bus?
Please let us know if there are concerns to operate in this way, great thanks for your help.