- Ask a related questionWhat is a related question?A related question is a question created from another question. When the related question is created, it will be automatically linked to the original question.
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
I'm comparing the INA128HD part from the INA128-HT family to the INA128U part from the INA128 family, as the INA128U is currently unavailable. Looking at the data sheet for both of these parts, it seems that the INA128HD part is equivalent to, if not better than, the INA128U part in most of the specifications we need to compare it to. However, it seems that the Offset Voltage (Vos) specification for the INA128HD part as well as some other electrical characteristics are very different than the INA128U part due to the INA128HD being a higher temp version and is tested differently. This spec is important in determining whether the INA128HD can be used in the circuit design.
Raymond Zhang1, a TI engineer, said that he's fairly sure that the two parts have the same SI die design per this forum: https://e2e.ti.com/support/amplifiers-group/amplifiers/f/amplifiers-forum/1252895/ina128-temperature-related-performance
However, when looking at the data sheet for both parts, the specifications seem to suggest otherwise:
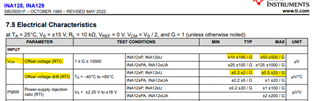
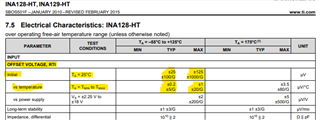
Can someone confirm if the INA128HD and INA128U have the same Si die design and if so, why there are such big differences between the two specs?
Erin
Currently the same die is used in both devices. The test and packaging is substantially different. The INA128HD has a 3 temperature test and the INA128U is only tested at 25C. This is the reason for the specification differences. It is possible in the future that the fab or die is updated. The INA128 is an old device and in some cases old devices are updated. Users of the device will get an update if this happens. Currently, however, the two devices you mention share the same die.
Art