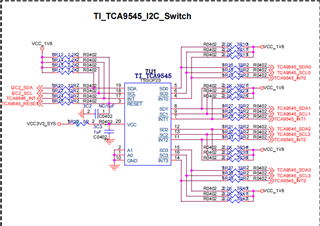
Part Number: TCA9545A
Now we are debugging TCA9545A based on RK3399. At present, we only know how to open the access I2C, but we do not know how to work and whether a driver is needed. If necessary, could you help to provide Linux driver and configuration?
thanks