Hi team,
Here's an issue from the customer may need your help:
Debug with other devices and find that other devices cannot receive CAN messages that are transmitted quickly and continuously due to device limitations. So the device needs to delay sending data for each ID. Delay with software and find that the intervals of CAN messages are not as delayed as expected when transmission is particularly frequent.
issue: how to set the interval between two frames of a message?
Could you help check this case? Thanks.
Best Regards,
Cherry



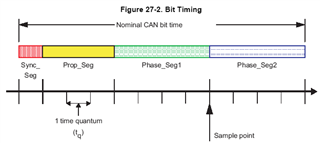 Where the Nominal Bit Time Tb=1/CAN BaudRate
Where the Nominal Bit Time Tb=1/CAN BaudRate