Hi Team:
There is a Pd calculation issue of TPS7B6950 and condition as below
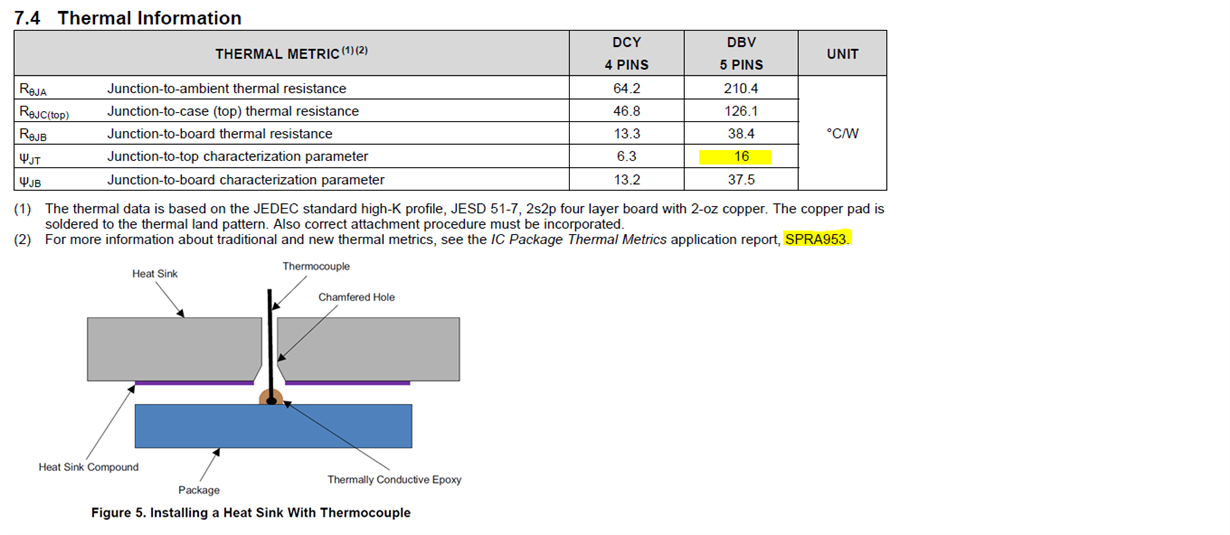
Vin=30.5V , Vout=5V , Iout=0.009 , Tc=90.9 °C , RθJC(top)=126.1 °C/W
PD=(30.5-5)*0.009=0.2295 , (0.2295*126.1)+90.91=119.8°C
As end customer rule , they will have 80% derating margin Tj=150*0.8=120°C so 119.8°C to close
Please help to confirm formula is right ? or any suggestion about formula or another better solution for this application , thanks.
Regards / Mark