Part Number: AM625
Tool/software:
Hi TI experts,
I see that there is a RTC module instance.
Do you have any guidance on the usage of the RTC
Part Number: J721S2XSOMXEVM
Tool/software:
How to enable wkup uart for for getting the boot logs?
Part Number: TDA4AEN-Q1
Tool/software:
Yocto build requires good internet connection, large storage space, large ddr memory on host pc and strong CPU. For small groups without a strong server, building yocto on a portable device like a removable disk and sharing between all co-workers can be an option.
Here explains how to build yocto on a removable disk and how to use the disk with a built yocto inside for other pc.
For yocto initial builder:
First of all, the external disk must be formatted as ext4. After plugging in the disk through usb port, the disk is likely to be auto mounted to /media/USER/{disk name}. Note that building yocto will always add your USER name into its generated makefile and environment configuration files. To avoid that, do remember to umount the disk and remount it to somewhere unrelated with your username like /opt
After the remounting, build yocto as normal.
For using disk on other PC:
Because the path is already written into the yocto project in the external disk, the mounting point should be the same as the initial yocto builder. So you should also umount the disk from the default mounting point and remount it to the same mounting point the initial builder uses.
Note: You can use docker to make the same.
You can also reach to the local FAE of processor if you have trouble building yocto and want someone to build it for you.
Regards,
Adam
Part Number: DRA821
Tool/software:
How to enable Falcon Boot Mode on 10.01 SDK?
Boot Flow:
R5 SPL -> ATF -> OPTEE -> U-BOOT -> Kernel
Regards
Gokul
Parts Discussed in Thread: AM62x, AM62Ax, AM62Dx, AM62Px
The primary role of the Device Management (DM) R5F core is to run the DM task. However, on some devices (not all devices!), TI supports writing custom code to run on the DM R5F, alongside the DM task.
Non-DM code running on the DM R5F should not interfere with the DM task in any way. That means the non-DM task should not crash the DM R5F core, block the DM task from running, corrupt DM memory, etc. If the DM task crashes, device management (DM) and power management (PM) requests fail. This can render the device inoperable until a power cycle resets the DM R5F.
These are best practices for customers who are writing custom code to run on the DM R5F.
Other resources
This information is planned to be added to the MCU+ SDK documentation under Developer Guides > Developing applications on Device Manager/Wake-up R5 core. Once the documentation has been updated, we will update this FAQ with links.
This is a helper FAQ for RE: [FAQ] DM R5F can crash in certain conditions: AM62x, AM62Ax, AM62Dx, AM62Px, AM67, AM67A question "We are writing custom DM R5F firmware. Could our design be affected?"
Parts Discussed in Thread: AM62x, AM62Ax, AM62Dx, AM62Px
The primary role of the Device Management (DM) R5F core is to run the DM task. However, there may be other non-DM code running on the DM R5F, alongside the DM task. The firmware running on the DM R5F core is initialized during boot time, either during SPL boot or SBL boot.
For more information about SPL boot and SBL boot, refer to the processor academy > Multicore > Boot flows: SBL vs SBL
AM62x || AM62Ax || AM62Px || AM64x
When using the SBL boot flow, the DM R5F initializes critical parts of the system, including the DM task. The SBL code may either close itself at that point, or it may load a runtime application into the DM R5F. The runtime application is selected based on address instead of being selected by filename. That means that if a runtime application is loaded, then you need to verify what application is flashed to the memory at that address.
Other FAQs
This is a helper FAQ for RE: [FAQ] DM R5F can crash in certain conditions: AM62x, AM62Ax, AM62Dx, AM62Px, AM67, AM67A question "SBL boot: How to find the DM R5F firmware that is loaded by SBL".
Part Number: TDA4AL-Q1
Tool/software:
Example application on SDK 10.0 to show large byte transfer between CDD IPC(MCU1_0) and Linux (A72) using cdd_ipc_rc_linux ,rpsmg_char_simple applications on J721S2 ?
Before Linux can communicate with a non-Linux core over the RPMsg inter-processor communication (IPC) protocol, several things needs to be true:
1) RPMsg between Linux and the non-Linux core must be supported by software drivers on both software instances
2) Application code to communicate over RPMsg must be written for both software instances
3) The Linux remoteproc driver must either initialize the core, or attach to the core (if the core is already running)
4) The RPMsg infrastructure (including VIRTIO buffers) must be initialized by Linux
For more information:
Running the out-of-the-box RPMsg test code:
refer to the processor academy > Linux > Evaluating Linux > IPC Example
AM62x || AM62Ax || AM62Px || AM64x
Examples of what "pass" and "fail" tests look like with the rpmsg_echo example:
[FAQ] Linux: How to check what binary is running on the DM R5F
Examples 1, 2, 3
Parts Discussed in Thread: AM62x, AM62Ax, AM62Dx, AM62Px, AM67, AM67A
The primary role of the Device Management (DM) R5F core is to run the DM task. However, there may be other non-DM code running on the DM R5F, alongside the DM task. The firmware running on the DM R5F core is initialized during boot time, either during SPL boot or SBL boot.
For more information about SPL boot and SBL boot, refer to the processor academy > Multicore > Boot flows: SBL vs SBL
AM62x || AM62Ax || AM62Px
We suggest one of these methods to check the binary:
Part Number: AM623
Tool/software:
Hi Expert,
When will AM62x have Functional safety certification document
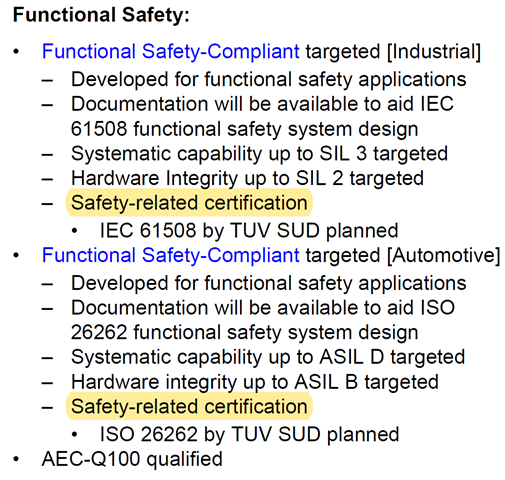
Thanks
Daniel