[Click here to return to Transceiver Homepage]
Welcome to the LVDS / M-LVDS Transceivers E2E page!
Listed below are a variety of resources to assist with the implementation of Low Voltage Differential Signaling, also know as LVDS!
LVDS / M-LVDS Basics:
M-LVDS:
Additional resources:
[Click here to return to Transceiver Homepage]
Welcome to the RS-485 / RS-422 Transceivers E2E page!
Listed below are a variety of resources to assist with the implementation of RS-485 and RS-422!
Note that many RS-485 resources also apply to RS-422
RS-485 / RS-422 Basics:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
IEC ESD, EFT, and Surge Information:
Special Functions of Select RS-485 devices:
Power Line Communication Using Powerbus (OOK modulated RS-485):
Part Number: LMH1297
Tool/software:
Hi,
When performing diagnostic evaluations of the LMH1297 retimer customers often want to adjust input cable EQ from the IO side. In these cases we recommend disabling the EQ adaptation and performing the following register sequence to manually adjust the cable EQ:
| Command | Register | Value | Mask |
| //Select the ConfigIO page | 0xFF | 0x05 | 0x05 |
| //Disable EQ Adaptation | 0x00 | 0xC0 | 0xC0 |
| //Write the cable EQ value | 0x24 | xx | 0x1F |
| //Read the cable EQ value | 0x25 | xx | 0x1F |
After writing the cable EQ value in ConfigIO register 0x24, read the updated value in 0x25 to ensure that the device's cable EQ value has changed.
Best regards,
Nick
[Click here to return to Transceiver Homepage]
Welcome to the CAN Transceivers E2E page!
Listed below are a variety of resources to assist with the implementation of the Controller Area Network, aka CAN!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Can 3.3V and 5V CAN transceivers operate on the same bus together?
My MCU uses 3.3V as the logic supply, do I need a 3.3V CAN transceiver?
What is CAN SIC (Signal Improvement Capability)? How does this improve my network?
What resources are available for programming with CAN controllers?
How can the power consumption of a CAN transceiver in active operation be calculated?
What are the different types of CAN implementations available in C2000 devices?
What is the difference between standard and split termination?
How do I find TI quality, reliability, and material reports?
When do I need to Isolate CAN? How do I use CAN isolated devices?
What power rating is needed for the CAN termination resistor?
TI Guides, Reports, and more:
Welcome to the Interface Transceivers E2E page!
Here you will find a variety of resources that support our long list of devices (750+ and counting!)
Select an interface below to find a collection of FAQs, application notes, videos, and more:
Part Number: DS320PR810
Tool/software:
How do I check to make sure my PCIe signals are AC-coupled correctly?
Part Number: DP83TC812S-Q1
Tool/software:
Hello,
Here is a summary of available information about RGMII Shift and Align mode for our DP83TC81x devices:
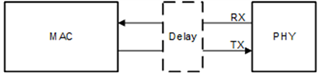
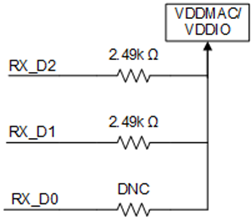
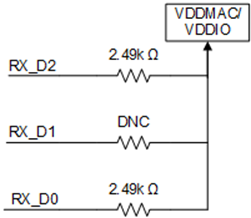
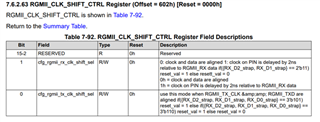
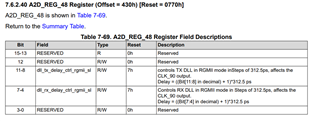
Part Number: LMH1239
Tool/software:
Hello SDI engineers and LMH enthusiasts,
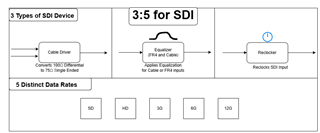
Figure 1 - 3:5 for SDI
In this E2E FAQ, I will be discussing GND plane layout best practices for SDI designs. In cable driver designs, see figure 1, SDI data transitions between 50 ohms differential and 75 ohm single ended characteristic impedances as the means of transport.
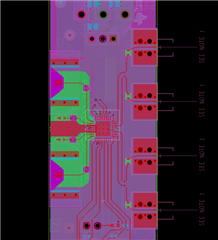
Figure 2 - LMH1297 layout
Figure 2 illustrates the way TI adjusts the PCB layout to content with this change in characteristic impedance change. The green section shows the GND reference at Layer 3 of the board for the 75 ohm single ended signals. The increase in distance between the traces and the reference plane increases the characteristic impedance on the trace.
All current must flow in a closed loop and return to its source. The goal of using a reference plane is to reduce emissions like crosstalk. The current will return to its source somehow, and it is in the designers best interest to ensure that the flow is predictable.
Best regards,
Nick
Part Number: TDP142
Tool/software:
Hi Experts,
What does 'Linear range' refer to on re-drivers like TDP142, TDP1204, TDP2004,...?
The device I received is marked as 'A5' but that is not listed as an option in the datasheet.
